Back
Blockchain Basics
Others
By HackQuest
Aug 23,20244 min read
Introduction to Blockchain
Definition
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. It enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof recording of data, which is essential for its widespread application in various industries beyond just cryptocurrencies.
Brief History
Blockchain technology was first conceptualized in 2008 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto and was implemented the following year as a core component of Bitcoin. Since its inception, blockchain has evolved from powering Bitcoin to a versatile technology with applications in numerous fields, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.
💡
GM! Here’s the summary of this article:
1. How Blockchain Works
2. Types of Blockchains
3. Key Features and Benefits
4. Blockchain Use Cases
5. Challenges and Considerations
6. Next Steps & Recommended Resources
If you prefer interactive learning/more thorough resources, please enroll in our basic learning track! It is 100% FREE and written by blockchain experts.
Let’s start with the basic structure of blockchain and how it works!
How Blockchain Works
Basic Structure
A blockchain is composed of a series of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. Each block is linked to the previous one through cryptographic hashes, forming a chain. This structure ensures that any alteration in one block would affect all subsequent blocks, making the blockchain immutable and secure.
Cryptographic Hashing
Cryptographic hashing is a fundamental feature of blockchain technology. It involves converting data into a fixed-size string of characters, which acts as a unique identifier for the data. This ensures that even a minor change in the input data results in a drastically different hash, providing security and integrity to the data stored on the blockchain.
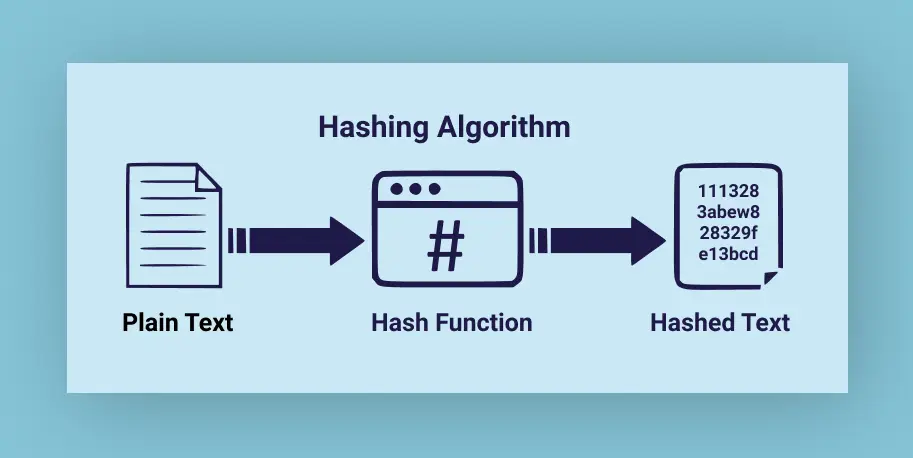
Source: Medium
Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and secure the network. The most common mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
PoW requires participants (miners) to solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks, ensuring security through computational effort.
PoS, on the other hand, selects validators based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral, providing a more energy-efficient alternative to PoW.
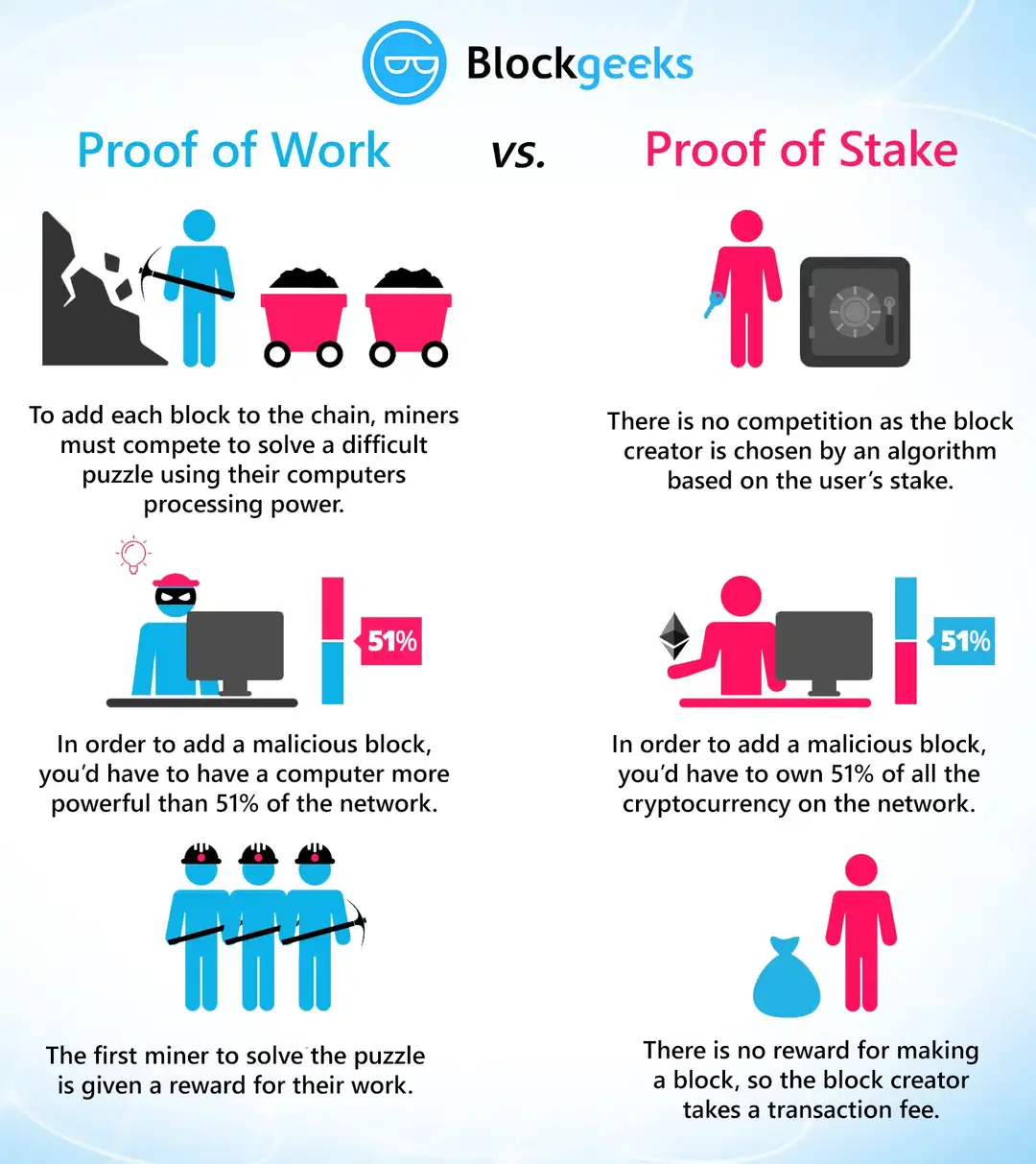
Source: Block Geeks
Types of Blockchains
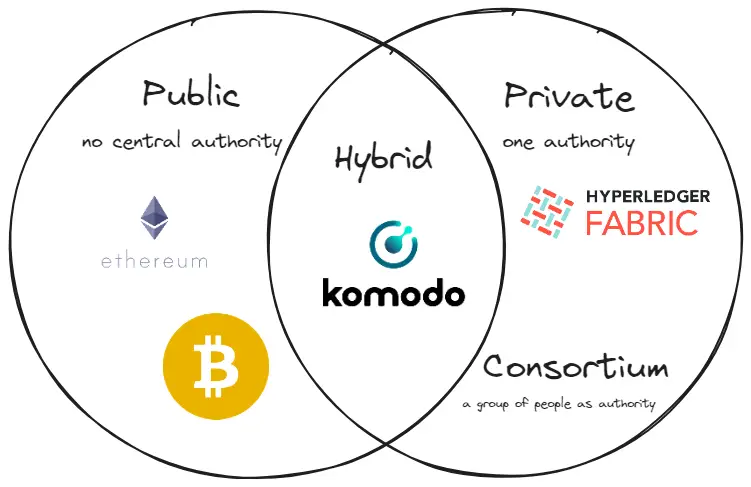
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone and operate in a fully decentralized manner. All transactions are visible to the public, ensuring transparency and security.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are restricted networks where access is controlled by a single organization or a group of entities. These blockchains offer greater control and faster transaction speeds, making them suitable for enterprise applications. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric, used by businesses for secure and efficient operations.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are controlled by a group of organizations rather than a single entity, providing a balance between decentralization and control. They are partially decentralized and have nodes from different organizations. Some examples of consortium blockchains include: R3, a group of financial institutions developing Corda, a blockchain-based solution to improve data sharing and upgrade the financial services industry; IBM Food Trust, a blockchain that connects entities in the food supply chain, such as growers, processors, distributors, and retailers, to improve transparency and traceability
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private blockchains, allowing for customizable levels of transparency and access. For example, an innovative cryptocurrency by the name of Swisscoin uses a hybrid blockchain that is based on blockchain technology and makes use of a unique trading system as well. Also, the hybrid blockchain used by XinFin has Ethereum for the public portion and Quorum for the secret portion. Their objective is to provide a platform for global trade and banking based on hybrid technology.
Six Key Features
Source: 101 Blockchains
Immutability
Blockchain's immutability ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature enhances the integrity and trustworthiness of the data stored on the blockchain. Every node in the system possesses a copy of the digital ledger. To add a transaction, each node must verify its validity. If the majority of nodes agree that it is valid, it is then added to the ledger. This process ensures transparency and prevents corruption.
Decentralized
Blockchain technology is decentralized, meaning it is maintained by a group of nodes rather than a central authority. This decentralization allows users to directly access and manage their assets, such as cryptocurrencies and important documents, using their private keys. The decentralized structure of blockchain empowers individuals by giving them control over their assets without relying on third parties.
The key benefits of blockchain’s decentralized nature include increased fault tolerance, user control, and resilience against malicious attacks. It eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries, reducing associated risks and preventing scams. Additionally, the transparent nature of blockchain ensures that all changes are visible, enhancing trust and authenticity within the system. For those interested in learning more about blockchain implementation and strategies, enrolling in a dedicated course can provide valuable insights.
Enhanced Security
Blockchain technology eliminates the need for a central authority, preventing any single entity from altering the network for personal gain. It combines decentralization with cryptography to enhance security. Cryptography, a complex mathematical algorithm, acts as a firewall against attacks by hashing every piece of information on the blockchain. This process disguises the true nature of the data, making it extremely difficult to tamper with.
Each block in the blockchain has a unique cryptographic hash and contains the hash of the previous block, making it nearly impossible to alter data without changing all subsequent hashes. Users have private keys for data access and public keys for transactions.
💥
Hashing is irreversible and highly resistant to corruption, as altering the network would require hacking millions of computers simultaneously. This robust security feature ensures that users' digital assets are well-protected against unauthorized access.
Distributed Ledgers
A public ledger in blockchain technology provides transparent information about transactions and participants, ensuring all activities are visible and cannot be hidden. Even in private or federated blockchains, where access is more restricted, multiple users still maintain oversight, contributing to the ledger's integrity. This decentralized maintenance by all users enhances the system's efficiency and reliability compared to traditional ledgers.
Key features of blockchain include its resistance to malicious changes and the equitable participation of all nodes in verifying transactions. No single user can alter the ledger unilaterally, and any suspicious activity is quickly detected. Every active node helps maintain and validate the ledger, ensuring no special privileges for any participant. This decentralized approach not only ensures a quick response to changes but also eliminates intermediaries, making updates almost instantaneous.
Consensus
Blockchain technology relies on consensus algorithms, which are central to its architecture and essential for network decision-making. These algorithms allow active nodes to agree on transactions quickly and efficiently, akin to a voting system where the majority decision prevails. This process ensures smooth operation, even with millions of nodes validating transactions, and maintains a trustless environment where nodes rely on the algorithms rather than each other.
Consensus algorithms contribute to the fairness and integrity of the blockchain network. Each algorithm has unique methods for decision-making, continually improving upon previous models to ensure effective and equitable outcomes. Maintaining decentralization, these algorithms are crucial for upholding the core values of blockchain, ensuring that all decisions are aligned with the network's principles.
Faster Settlement
Traditional banking systems are often slow, sometimes taking days to finalize transactions and settlements, and are prone to corruption. Blockchain technology offers a faster alternative, enabling quicker money transfers, which is particularly beneficial for foreign workers sending money home to their families. This expedited process can be crucial in times of need, providing a more efficient and reliable means of international remittance.
Additionally, blockchain's smart contract system facilitates faster settlements for various contracts, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction fees. Although the technology faces challenges in handling a high volume of users simultaneously, ongoing improvements aim to enhance its efficiency. The impact of blockchain on international trade and personal transactions highlights its importance and potential benefits.
Basic Web3 Terms
💥
Find these glossary terms useful and want to learn more? Check out our glossary page for more details!
Blockchain Use Cases
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is long known as the most heard of application of web3. It is a financial ecosystem that operates on blockchain technology, utilizing smart contracts to automate services and eliminate traditional intermediaries like banks and brokers. This technology ensures that all transactions are transparent, permissionless, and accessible to anyone with internet access. DeFi's key advantages over traditional centralized finance (CeFi) include enhanced accessibility, transparency, security, efficiency, and innovation. It provides borderless financial services, crucial for regions lacking adequate banking infrastructure, and records transactions publicly on the blockchain, enabling verification and reducing hidden fees. Additionally, advanced encryption technologies protect funds and transactions, while smart contracts streamline processes, increasing operational efficiency. The open development platform of DeFi fosters innovation, attracting global developers and encouraging rapid technological advancement. Its distributed structure enhances system resilience, ensuring continuous operation even if some nodes are compromised.
Payment
An example of a DeFi payment project is BitPay, a payment gateway that offers merchants the availability to accept funds using Bitcoin.
BitPay revolutionizes digital payments by leveraging blockchain technology to enable seamless and secure cryptocurrency transactions. As a leading payment service provider, BitPay allows businesses and individuals to accept Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as payment, ensuring fast and efficient processing. With its user-friendly interface, BitPay simplifies the process of receiving, storing, and spending digital currencies. The platform's integration capabilities allow merchants to incorporate cryptocurrency payments into their existing systems easily. BitPay also offers tools for invoicing, payment tracking, and financial reporting, making it a comprehensive solution for managing digital payments. By eliminating the need for traditional financial intermediaries, BitPay reduces transaction fees and enhances the security and transparency of payments, providing a reliable and cost-effective alternative for global transactions.
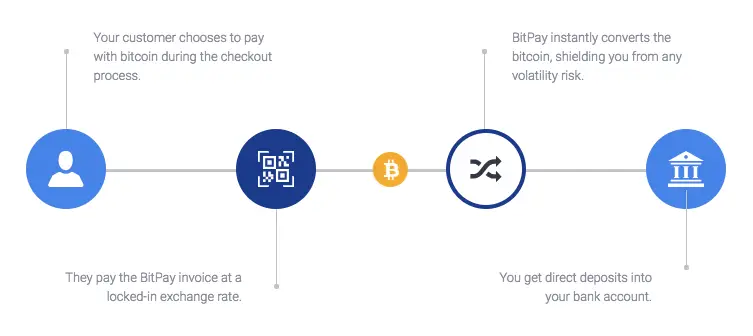
Source: BitPay Docs
Lending
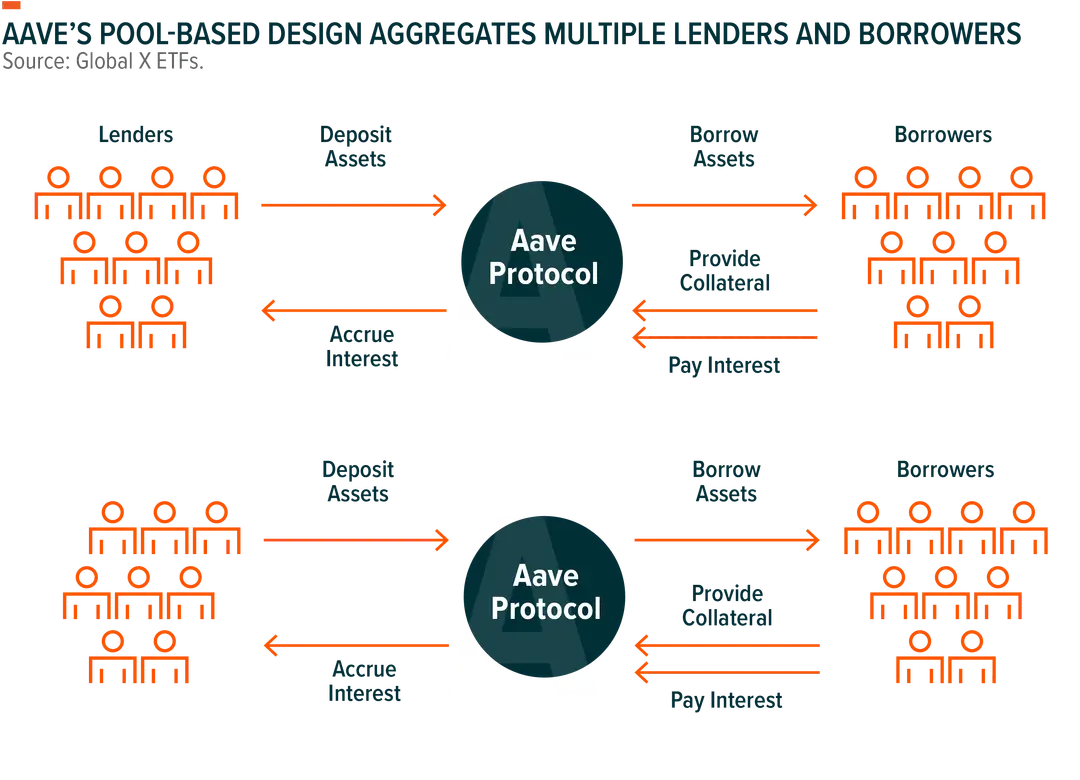
Aave is an example of DeFi lending project.
Aave liquidity protocol revolutionizes the lending and borrowing landscape by utilizing blockchain technology to create a decentralized, trustless financial ecosystem. As an open-source liquidity protocol, Aave allows users to lend and borrow a wide range of cryptocurrencies without the need for a traditional financial intermediary. Lenders can deposit their digital assets into liquidity pools to earn interest, while borrowers can take out loans by providing collateral, all facilitated by smart contracts that automate and secure the transactions. Aave's innovative features, such as flash loans and credit delegation, offer unprecedented flexibility and efficiency in financial transactions. Flash loans enable users to borrow instantly without collateral, provided the liquidity is returned within the same transaction. Credit delegation allows trusted users to borrow without directly posting collateral, based on an agreement with the lender. By eliminating the need for traditional banks and reducing the barriers to access credit, Aave promotes financial inclusion and empowers users with greater control over their assets.
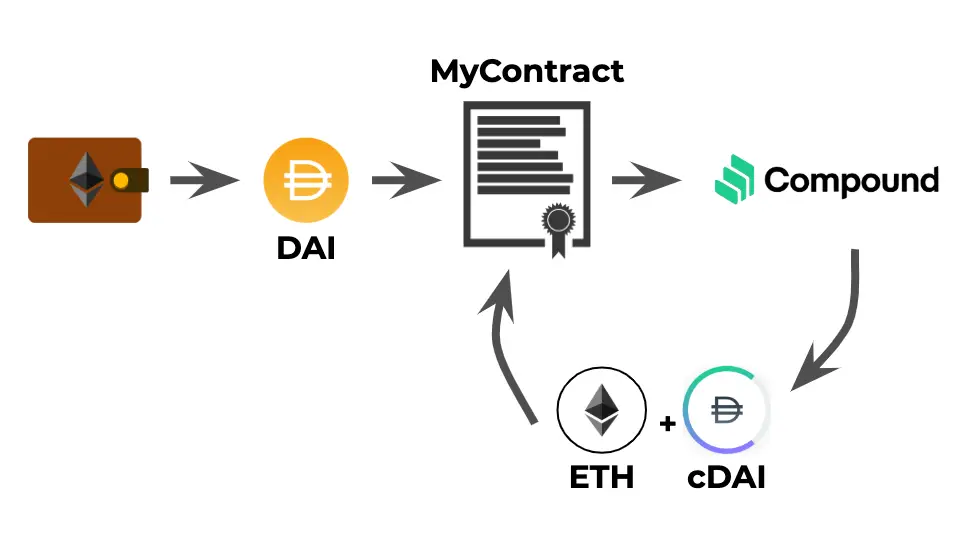
Another example is Compound, an algorithmic, autonomous interest rate protocol built for developers, to unlock a universe of open financial applications.
Compound transforms the traditional lending and borrowing model by creating a decentralized platform where users can earn interest on their cryptocurrencies or borrow assets against their holdings. As an automated, algorithmic money market, Compound allows users to supply cryptocurrencies to liquidity pools and earn interest based on the demand for borrowing those assets. Borrowers can access these liquidity pools by providing collateral, with interest rates dynamically adjusting based on real-time supply and demand. Compound's smart contracts handle all transactions, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency without the need for traditional financial intermediaries. This system promotes greater financial inclusion by enabling users to participate in the lending and borrowing market directly, offering a more flexible and accessible alternative to conventional banking services. By utilizing blockchain technology, Compound empowers users to maximize the utility of their digital assets, making it a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem.
Trading
A prominent example of a DeFi project is Uniswap, a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on the Ethereum blockchain.
Uniswap employs an automated market maker (AMM) model, allowing users to trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Users (liquidity providers) deposit token pairs into liquidity pools, facilitating trades. When users wish to exchange tokens, the smart contract automatically executes the trade at the current rate, transferring the specified amount. This trustless system reduces the risk of fraud and intermediary interference, highlighting the potential of DeFi to revolutionize the financial domain. While challenges such as poor user experience and regulatory issues persist, DeFi's technological advancements promise an increasingly significant role in the future financial industry.
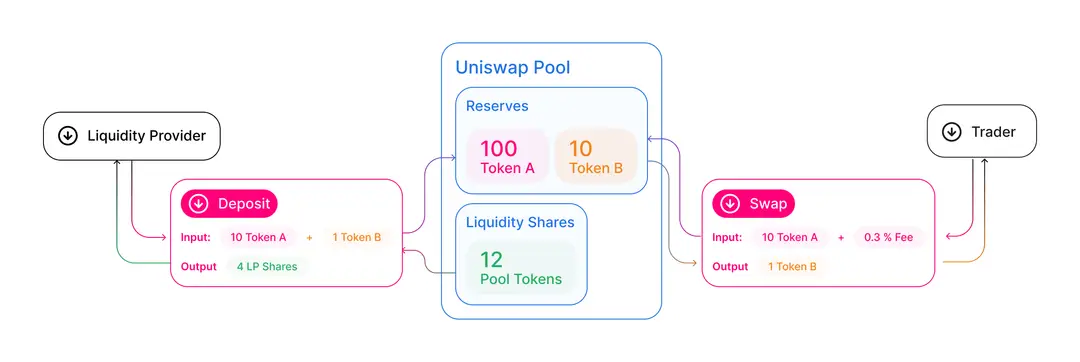
Source: Uniswap Docs
Another example is Doo, an On-Chain Liquidity Provider for everyone.
DODO is a decentralized trading platform that leverages blockchain technology to offer an innovative and efficient solution for cryptocurrency trading. Using its unique Proactive Market Maker (PMM) algorithm, DODO provides high liquidity and low slippage, ensuring a seamless trading experience for users. Unlike traditional automated market makers (AMMs), DODO's PMM algorithm adjusts the market price based on real-time supply and demand, resulting in more accurate pricing and reduced impermanent loss for liquidity providers. Users can trade a wide range of cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without needing an intermediary, maintaining full control over their assets. DODO also supports customizable liquidity pools, allowing users to create and manage their own trading pairs and liquidity parameters. By enhancing liquidity and optimizing trading efficiency, DODO is a key player in the DeFi ecosystem, democratizing access to decentralized trading and fostering a more inclusive financial market.

Source: Creative Fabrica
Let’s look at another trading platform: Pancake. Developers trade, earn, and own crypto on the all-in-one multichain DEX.
Pancake utlized an automated market maker (AMM) model, PancakeSwap allows users to trade directly from their wallets by interacting with smart contracts, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Liquidity providers can earn rewards by depositing their tokens into liquidity pools, which are used to facilitate trades on the platform. PancakeSwap also offers additional features such as yield farming, staking, and participation in lottery games, enhancing the overall DeFi experience. Its low transaction fees and high-speed operations on the Binance Smart Chain make it an attractive option for traders and liquidity providers alike. By providing a decentralized and efficient trading environment, PancakeSwap democratizes access to financial services and supports the growth of the DeFi ecosystem.

Source: Airdrop Alert
Stablecoin
DAI, a stablecoin created by MakerDAO, is a cornerstone of the decentralized finance ecosystem, providing stability and reliability in the volatile cryptocurrency market.
Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, DAI is pegged to the US dollar, maintaining a 1:1 value ratio. This stability is achieved through a system of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, where users can lock up collateral in the form of cryptocurrencies to generate DAI. This collateral-backed mechanism ensures that DAI remains stable, even during significant market fluctuations. MakerDAO’s decentralized governance allows MKR token holders to participate in key decisions, such as setting risk parameters and interest rates, ensuring the system's robustness and adaptability. By providing a stable digital currency, DAI enables users to engage in everyday transactions, trading, and lending without the risk of volatility, making it a crucial tool for financial inclusion and stability within the DeFi landscape.
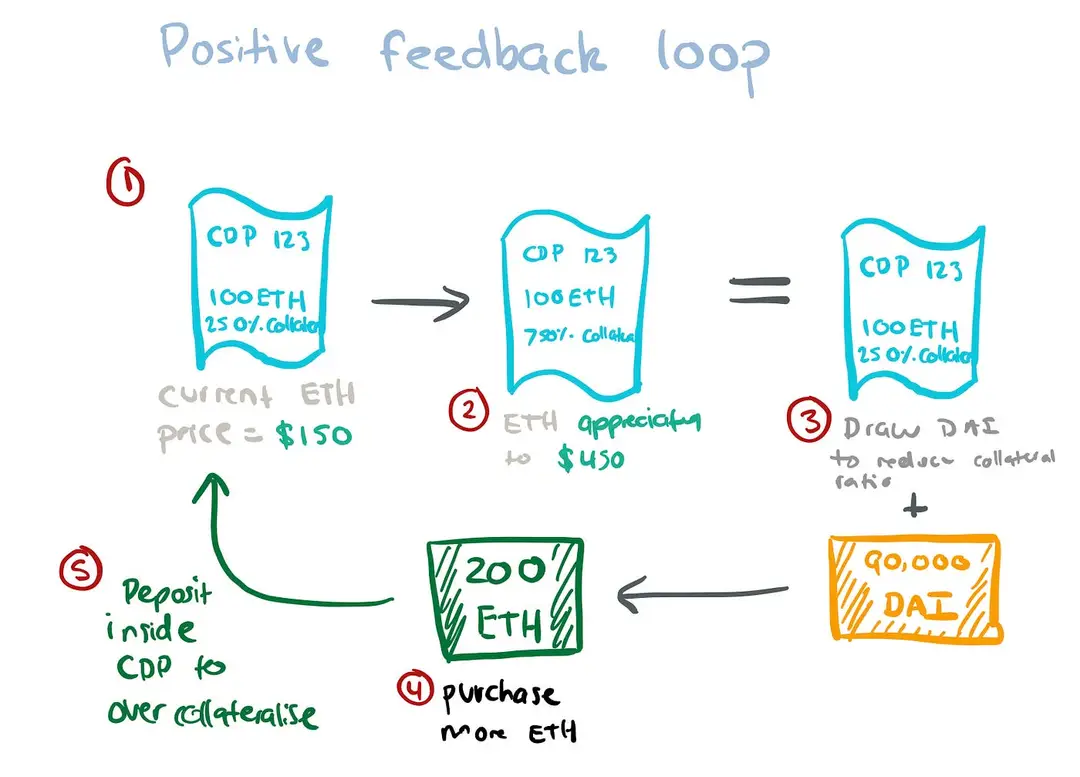
Source: Medium
Gaming
Web3 Gaming represents the next evolution of the gaming industry, leveraging blockchain technology to create decentralized, transparent, and player-centric gaming ecosystems. Unlike traditional gaming, where game assets and data are controlled by centralized entities, Web3 Gaming utilizes smart contracts to ensure that all in-game transactions and ownership records are transparent and immutable. This technology empowers players with true ownership of their digital assets, such as characters, items, and virtual real estate, which can be traded or sold on various platforms. Key advantages of Web3 Gaming over traditional gaming include enhanced transparency, security, and innovation. By eliminating centralized control, players have more control over their assets and can interact directly with the gaming ecosystem without intermediaries. Advanced encryption technologies protect game data and transactions, ensuring a secure gaming environment. The decentralized structure of Web3 Gaming fosters innovation, attracting developers to create novel gaming experiences and economic models. This player-driven approach is reshaping the gaming landscape, making it more inclusive, fair, and engaging for all participants.
One example is fully on-chain games, the forefront of Web3 Gaming. They leverage blockchain technology to ensure that every aspect of the game, from assets to game logic, is stored and executed on the blockchain. This complete decentralization provides unparalleled transparency, security, and player ownership. Unlike traditional games where critical data is managed by centralized servers, fully on-chain games utilize smart contracts to handle all game operations, ensuring that game mechanics are tamper-proof and fair. Players have true ownership of in-game assets, which are represented as NFTs and can be freely traded or sold on various marketplaces. The immutable nature of blockchain technology ensures that game data is secure and transparent, preventing cheating and ensuring that all players have a level playing field. This innovative approach not only enhances the gaming experience but also fosters a more engaged and empowered player community, driving the future of the gaming industry toward greater inclusivity and innovation.
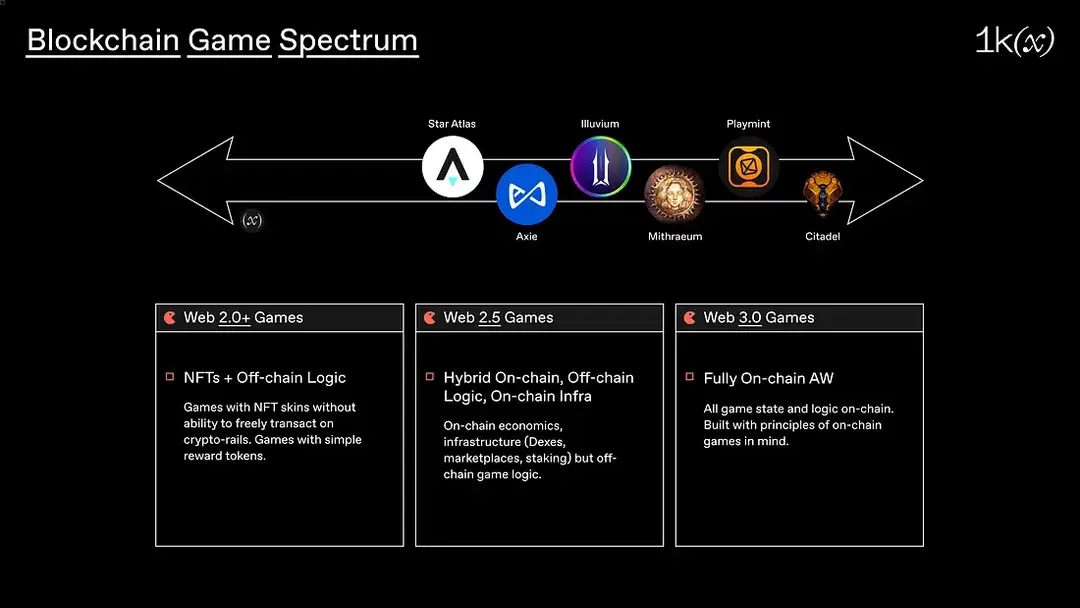
Source: Orochi Network
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain enhances supply chain management by providing transparent and immutable records of transactions. It improves traceability, accountability, and efficiency, helping to verify product origins, reduce fraud, and streamline logistics.
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) leverage blockchain technology to transform supply chain management by decentralizing the physical infrastructure that underpins it.
Helium revolutionizes supply chain management through its innovative decentralized physical infrastructure network (DePIN). By utilizing blockchain technology, Helium creates a decentralized wireless network, known as The People's Network, which is maintained by individuals using Helium Hotspots. These Hotspots provide long-range wireless coverage for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enhancing connectivity and data transmission across various industries. This decentralized approach ensures a more resilient and scalable infrastructure, eliminating single points of failure and enhancing overall network reliability.
Helium's blockchain-based system offers significant advantages for supply chain management. It provides a transparent and immutable record of data transmission, ensuring that all information is verifiable and tamper-proof. This enhances traceability and accountability within the supply chain, reducing the risk of fraud and improving the integrity of data. By decentralizing network infrastructure, Helium also reduces costs and increases accessibility, enabling a broader range of participants to benefit from advanced connectivity solutions. This innovative approach not only improves operational efficiency but also fosters a more inclusive and robust supply chain ecosystem.
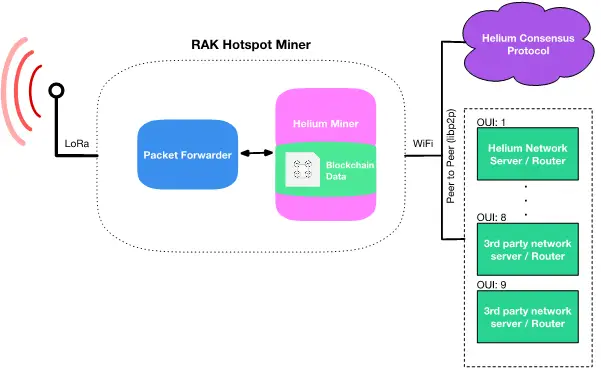
Source: News-RAK
Art & Entertainment
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the art and entertainment industries through the use of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and enhanced protection of intellectual property (IP). NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of a specific item or piece of content, such as art, music, or videos, and are stored on the blockchain. This ensures that each NFT is one-of-a-kind and cannot be duplicated, providing verifiable proof of ownership and authenticity.
For example, Azuki NFTs are a unique collection of digital art pieces that exemplify the innovative use of blockchain technology in the art and entertainment industries. Each Azuki NFT represents a distinct digital artwork, combining various artistic styles and themes, including samurais and skateboarders. These NFTs are stored on the blockchain, ensuring their authenticity and scarcity. By leveraging blockchain, Azuki provides verifiable proof of ownership and provenance, which is crucial in the digital art market.
The Azuki NFT collection highlights the transformative potential of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in providing artists with new revenue streams and greater control over their work. Artists can tokenize their creations, sell them directly to collectors, and earn royalties on secondary sales through smart contracts. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for intermediaries, ensuring that artists retain a larger share of the profits. The integration of blockchain technology not only secures the ownership and transfer of digital art but also fosters a more transparent and inclusive art ecosystem.

Source: Forbes
Education
Blockchain technology is poised to transform the education sector by providing secure, verifiable credentials and enhancing the reputation management of institutions and individuals. Blockchain can store and verify educational certificates, degrees, and achievements, ensuring their authenticity and preventing fraud. This decentralized approach makes it easier for employers and other educational institutions to verify qualifications, enhancing trust and efficiency in the hiring and admissions processes.
Open Campus leverages blockchain technology to revolutionize education through its decentralized governance model, enhancing the transparency, security, and efficiency of educational credentials and reputation management. By utilizing a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), Open Campus enables a community-driven approach to decision-making, where stakeholders, including students, educators, and institutions, can participate in the governance process. This ensures that the educational ecosystem is responsive to the needs and feedback of its participants, fostering a more inclusive and democratic environment.
The blockchain-based platform allows for the secure storage and verification of educational credentials, ensuring their authenticity and preventing fraud. This decentralized approach simplifies the process of credential verification for employers and other educational institutions, making it more efficient and trustworthy. Additionally, by using smart contracts, Open Campus can automate the issuance and management of certificates, providing tamper-proof records that are easily accessible and shareable. This innovative use of blockchain technology in education promotes lifelong learning and empowers individuals with verifiable, portable credentials that enhance their career opportunities and educational experiences.
💥
HackQuest is another web3 application in education. Check out our content here:
Identity
Digital Identity
Blockchain offers a secure way to manage digital identities, protecting personal information and enabling individuals to control their data. This can prevent identity theft and provide a reliable method for verifying identities online.
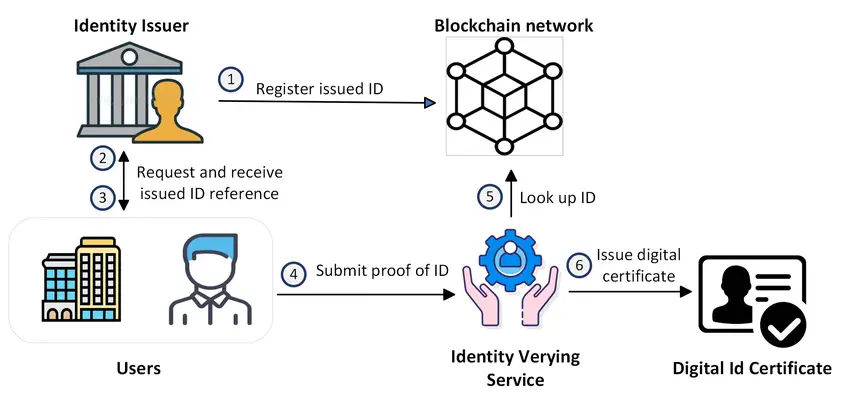
Source: ResearchGate
Aspecta ID utilizes blockchain technology to provide a decentralized and secure solution for digital identity management, enhancing privacy, security, and user control. Decentralized Identity (DID) systems offered by Aspecta ID enable individuals to own and manage their personal data without relying on centralized authorities. This ensures that users have full control over their identity information, which is stored on the blockchain, making it immutable and verifiable.
Aspecta ID's platform allows users to create, manage, and share their digital identities securely. It supports various use cases, including voting, where blockchain ensures transparent and tamper-proof election processes by recording votes immutably. This technology can enhance trust in democratic systems by providing end-to-end transparency from voter registration to vote counting. Additionally, Aspecta ID can be used in charitable donations, ensuring that contributions are transparent and reach their intended recipients without being diverted. By decentralizing identity management, Aspecta ID enhances security, privacy, and trust across multiple applications, empowering users and fostering greater accountability in digital interactions.
Voting Systems
Blockchain can enhance the security and transparency of voting systems by creating an immutable record of votes. This technology ensures that each vote is accurately counted and prevents tampering, increasing trust in the electoral process.
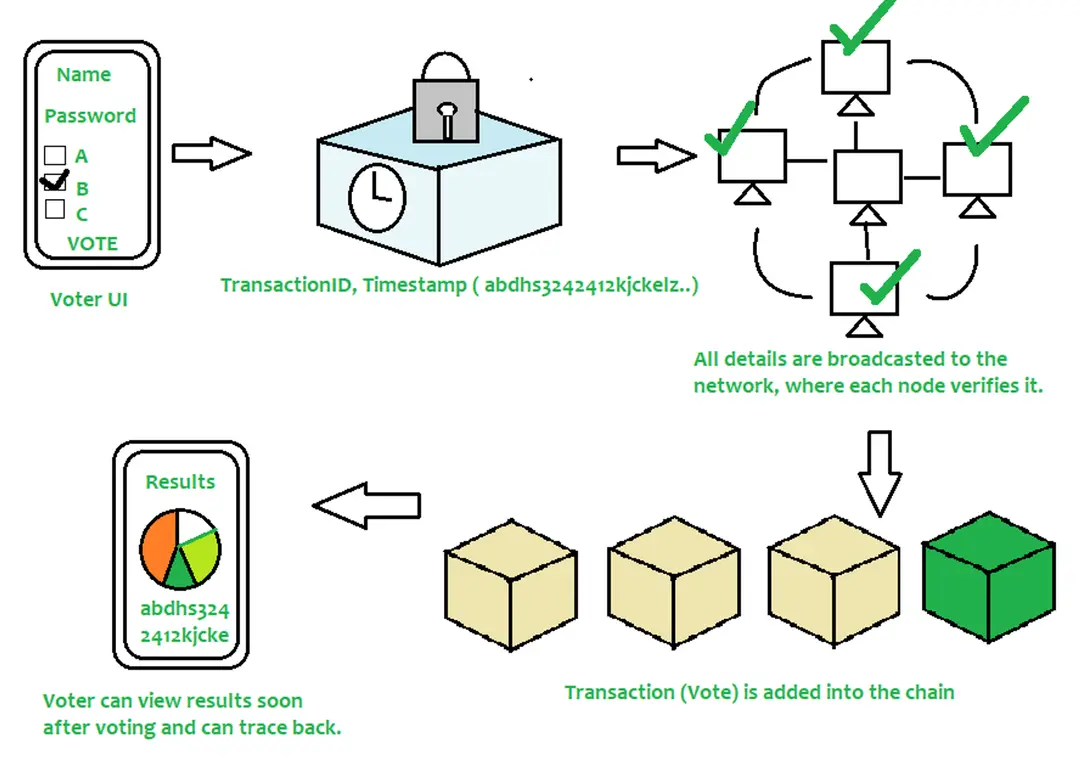
Source: GeeksforGeeks
In the context of voting, blockchain technology ensures transparent and tamper-proof election processes by recording votes immutably, enhancing trust in democratic systems. Blockchain voting systems provide end-to-end transparency, from voter registration to vote casting and tallying, making it virtually impossible to alter votes without detection. Each vote is encrypted and linked to a unique identifier, ensuring that it can be verified and counted accurately while maintaining voter anonymity. This level of transparency and security addresses many of the issues faced by traditional voting systems, such as fraud and manipulation, and enhances voter confidence in the electoral process.
Similarly, blockchain-based charity platforms provide transparency and accountability, ensuring that donations reach their intended recipients without being diverted or misused. By decentralizing identity and related services, blockchain technology enhances security, privacy, and trust across various applications, from personal identification to civic participation and charitable activities.
💡
One of our previous users actually designed a voting system in his recent hackathon. Want to know what he developed and his learning journey? Check out this article:
Others
Blockchain technology is making significant inroads in many other sectors, including healthcare and real estate, by leveraging its decentralized and secure framework. In healthcare, blockchain can provide secure, interoperable medical records, improving patient care and enabling better data sharing among healthcare providers. This ensures that patient information is accurate, up-to-date, and accessible only to authorized personnel, enhancing privacy and security. Blockchain also facilitates the tracking of pharmaceuticals and medical supplies, ensuring their authenticity and preventing counterfeiting. By providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions, blockchain technology enhances trust and efficiency within the healthcare system.
In real estate, blockchain facilitates transparent and efficient property transactions by providing a tamper-proof record of ownership and transactions. Smart contracts can automate the process of buying, selling, and leasing properties, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing the risk of fraud. This not only speeds up the transaction process but also reduces costs associated with traditional real estate transactions. Projects like Propy are pioneering the use of blockchain in real estate, enabling faster and more secure property transactions. By addressing challenges in these diverse sectors, blockchain technology continues to demonstrate its versatility and potential to create more efficient, secure, and transparent systems across various industries.
Challenges and Considerations
Blockchain Trilemma: The challenge of achieving decentralization, scalability, and security simultaneously in blockchain networks
In essence, it is difficult to optimize all three aspects at once. Decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the network, promoting trust and resilience. Scalability refers to the network's ability to handle a growing number of transactions efficiently. Security ensures that the network is resistant to attacks and fraud. Often, improving one of these aspects can lead to compromises in the others, posing a significant challenge for blockchain developers and researchers.
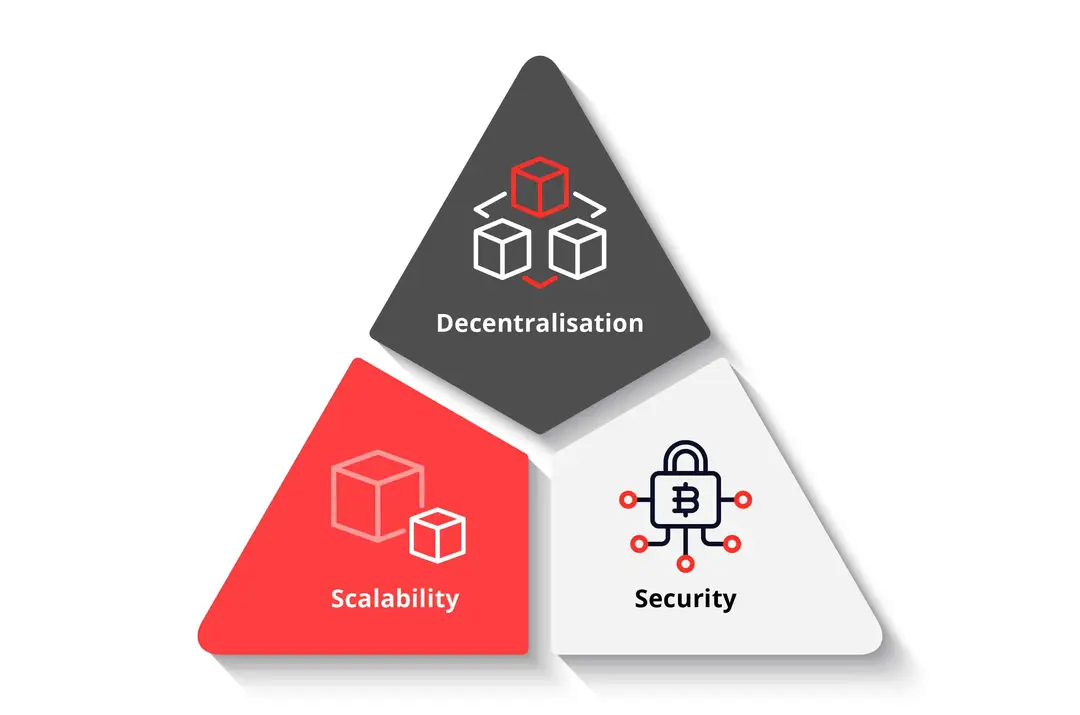
Source: DBS Bank
Regulatory Concerns
The regulatory landscape for blockchain is continually evolving. Different countries have varying regulations that impact blockchain adoption, particularly regarding compliance, privacy, and legal recognition of blockchain transactions. Web3 aims to create a decentralized internet infrastructure, but its lack of a central authority poses significant challenges to traditional regulatory frameworks designed for centralized entities. This decentralization complicates regulatory compliance, especially in areas such as user protection and the prevention of illegal activities.
One of the primary challenges highlighted is balancing user privacy with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, which require detailed user information that often conflicts with the anonymous nature of blockchain transactions. Additionally, the global nature of blockchain technology necessitates navigating varying regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. Experts advocate for a balanced approach to regulation that protects users without compromising the core principles of decentralization. Collaboration between regulators and the Web3 community is essential to develop frameworks that ensure compliance while fostering innovation in the decentralized web ecosystem.
Energy Consumption
The environmental impact of Web3 technologies is a significant concern as blockchain and decentralized networks continue to grow. Web3, which emphasizes decentralization and transparency, relies heavily on blockchain technology, which can be energy-intensive. The most notable example is the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which requires substantial computational power and, consequently, high energy consumption. This has led to increasing scrutiny over the carbon footprint associated with blockchain operations.
However, the Web3 community is actively exploring more sustainable alternatives. Proof-of-stake (PoS) is one such alternative, offering a more energy-efficient consensus mechanism that significantly reduces the environmental impact. PoS and other emerging technologies aim to maintain the security and decentralization of blockchain while minimizing energy use. Additionally, initiatives are underway to use renewable energy sources for blockchain operations, further mitigating their environmental footprint. As Web3 evolves, balancing technological advancement with environmental sustainability remains a critical focus, driving innovations that aim to create a greener, more sustainable decentralized future.
Enjoy what you’ve read so far, and want to learn more about blockchain? We’ve got you covered!
💡
Or start diving into the basics of blockchain today with our Web3 Basics Learning Track!
💡
Check out our Introduction to Blockchain and Smart Contracts: A Technical Perspective MOOC with NTU
Next Steps & Recommended Resources
Now you should have a basic understanding of blockchain, so what’s next?
Knowledge of deploying smart contracts is a MUST in web3, especially if you want to participate in hackathons. If you still don’t have a clear idea of how it works, check out our ecosystem learning tracks to learn more!
We also have many other resources for you to learn more about blockchain in different formats: