Back
NTU MOOC Study Notes - Session 4 Web3 Landscape (III): DeFi
Study Notes
By HackQuest
Jun 17,20244 min readDate: 9-10:30 AM SGT, June 18th 2024 / 9-10:30 PM EST, June 17th 2024
Session Title: Web3 Landscape (III): DeFi
NTU I&E x HackQuest MOOC is free and open to all individuals interested in Web3. The MOOC is led by top voices in crypto including Yat Siu (Co-founder, Animoca), Ed Felten (Co-founder, Offchain Labs), Sergey Gorbunov (Co-founder, Axelar), Scott Moore (Co-founder, Gitcoin), Haider Rafique (CMO, OKX), Austin Griffith (Developer Onboarding, Ethereum Foundation), Anna Yuan (Stablecoins Lead, Solana Foundation), and many more. For those who prefer having a text summary and review material, this study note provides a recap of what’s covered during the MOOC. Happy learning!
Overview
Main Topic: The Origin, Evolution, Key Concepts and Future Outlook of DeFi
Objectives:
1.Explore the origin and evolution of DeFi.
2.Examine the core components and advanced concepts within DeFi.
3.Analyze current trends and the future outlook of DeFi.
Section 1: Introduction to DeFi
1.1 Understanding Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a paradigm shift in how financial services are structured and delivered. Unlike traditional finance, which relies on centralized institutions like banks and exchanges, DeFi operates on decentralized networks, primarily using blockchain technology. This shift enables peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, fostering a more open and inclusive financial ecosystem.
1.2 Key Characteristics of DeFi
●Permissionless Access: Anyone with an internet connection can participate in DeFi platforms, without the need for approval from centralized authorities.
●Transparency: Transactions and smart contracts on the blockchain are publicly verifiable, ensuring transparency and trust.
●Interoperability: DeFi protocols can interact seamlessly with each other, allowing for complex financial products and services to be built by combining different protocols.
1.3 Importance of DeFi
DeFi democratizes access to financial services, providing opportunities for individuals in underbanked regions to engage in economic activities. It also fosters innovation in financial products, offering new ways to save, borrow, trade, and invest.
Section 2: The Origin and Evolution of DeFi
2.1 The Origin of DeFi
The concept of decentralized finance (DeFi) emerged from early experiments in applying blockchain technology to financial scenarios. One of the pivotal developments was the creation of Automated Market Makers (AMMs), designed to overcome the limitations of centralized exchanges. AMMs enabled permissionless trading and lowered barriers for asset issuers, fundamentally altering how trading and liquidity provision could be approached.
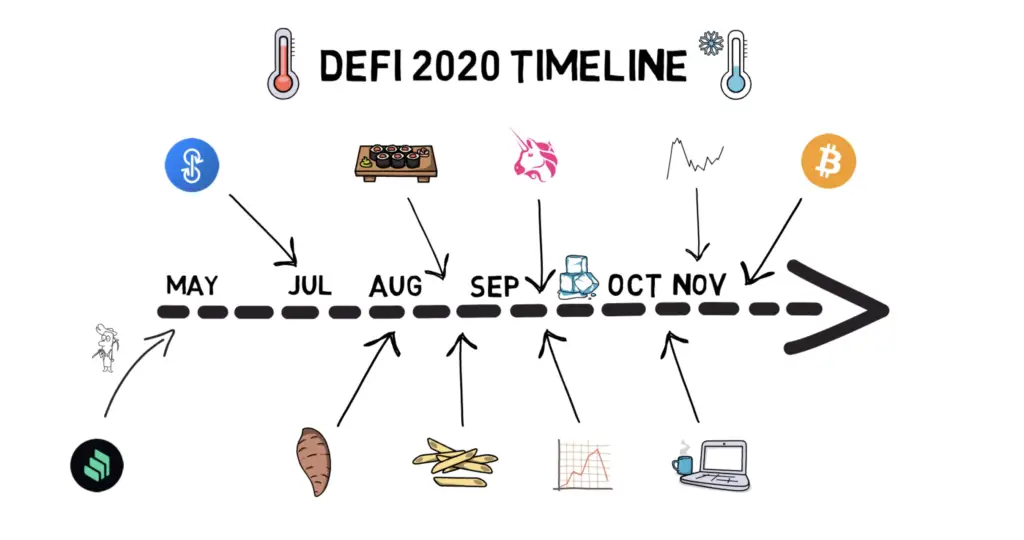
2.2 DeFi Summer 2020
The summer of 2020 marked a significant period known as "DeFi Summer," characterized by the rapid rise of platforms like Uniswap. These platforms facilitated the creation and trading of tokens on a massive scale. Key features that fueled this growth included self-custody, transparency, and permissionless access, which collectively democratized financial participation and innovation.
Section 3: Core Components of DeFi
3.1 Stablecoins
Types of Stablecoins:
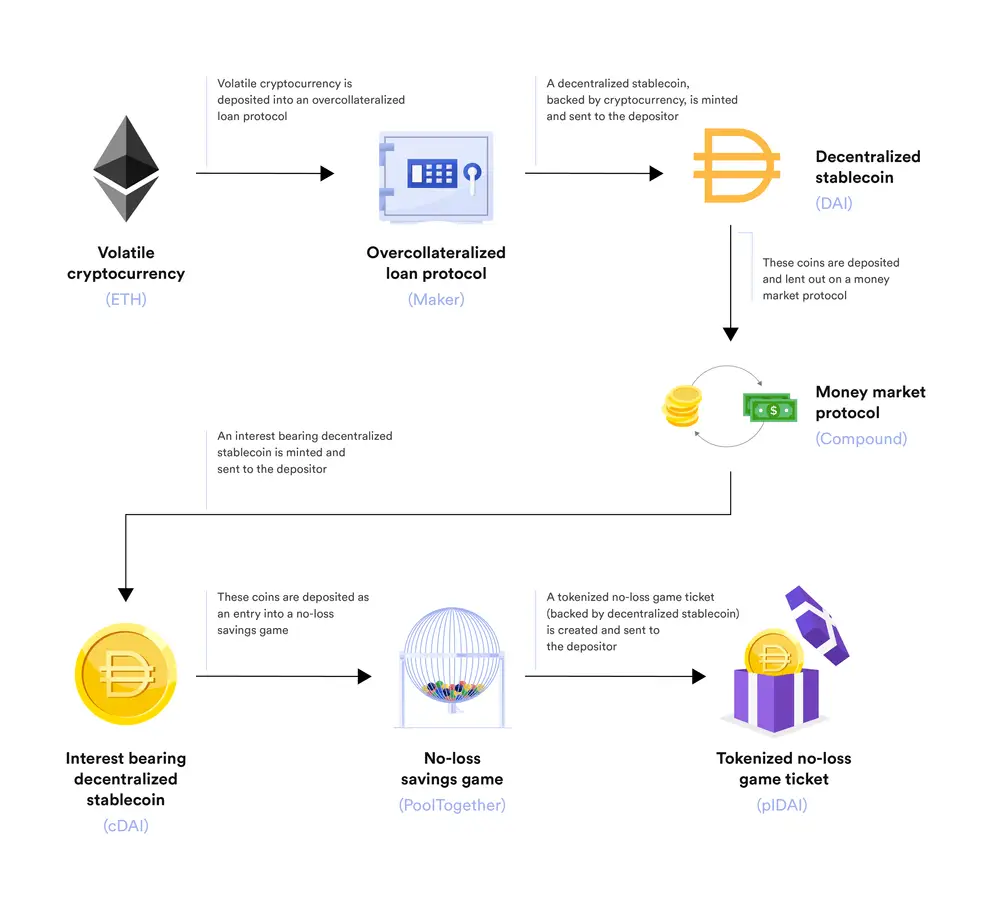
2.Decentralized Stablecoins (e.g., DAI): These use crypto collateral to maintain their value, relying on smart contracts and algorithms to ensure stability.
3.2 Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges have evolved from order book-based models to AMMs, which offer improved capital efficiency. Examples include Uniswap (classic AMM), Curve (specialized in stablecoin trading), and DODO (proactive market making).
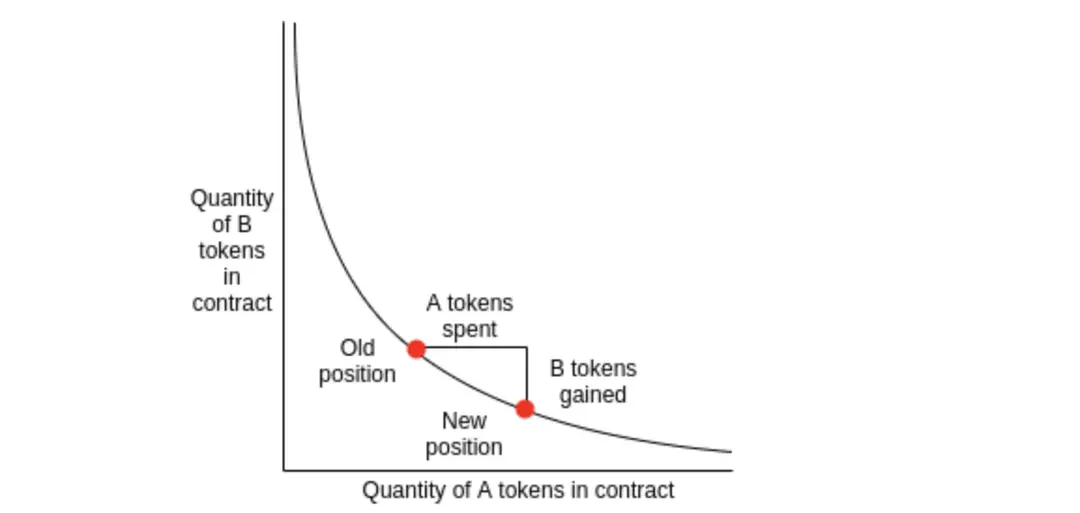
3.3 Lending Protocols
The lending protocols in DeFi have shifted from peer-to-peer models to peer-to-pool models, significantly enhancing liquidity. Notable protocols in this space are Compound, Aave, and MakerDAO.
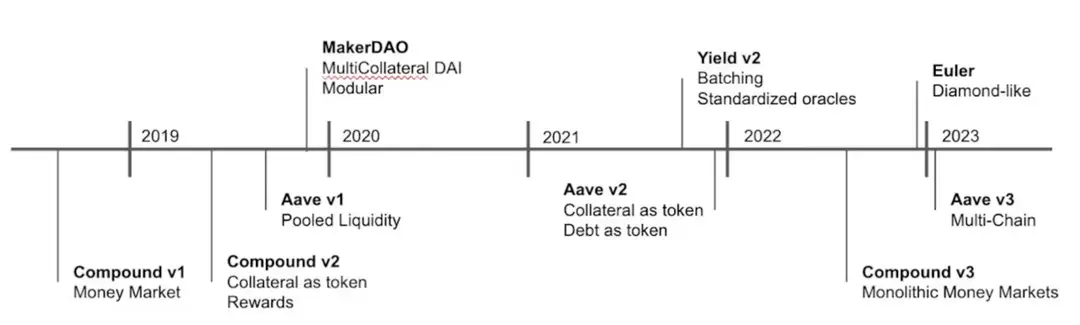
Section 4: Advanced DeFi Concepts
4.1 Composability
Composability refers to the ability to integrate various DeFi protocols to create new financial products and services. An example is combining lending and DEX protocols to facilitate margin trading.
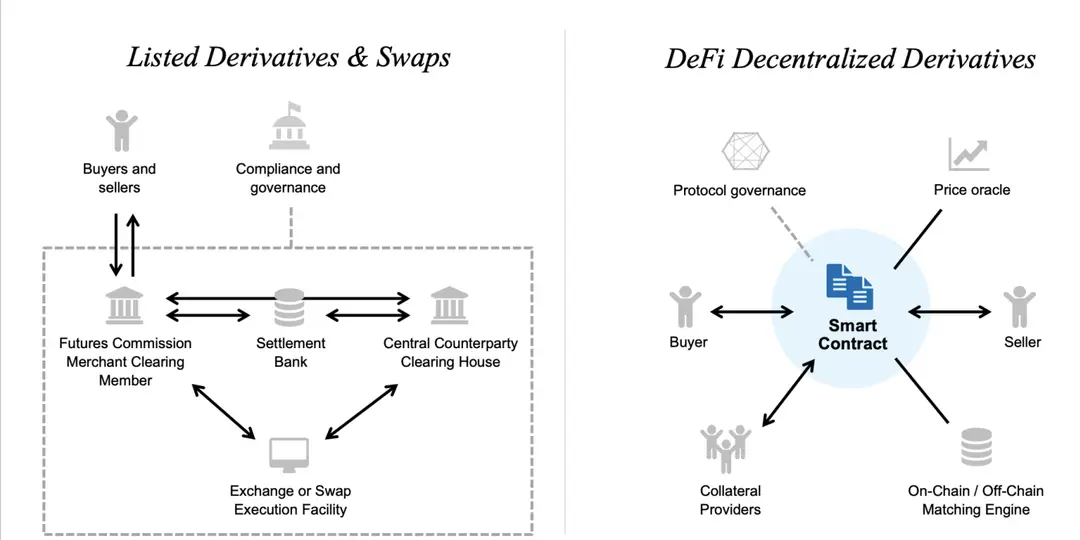
4.2 Derivatives
DeFi derivatives involve using futures, options, and perpetual contracts for risk management and speculation. GMX, a pool-based perpetual trading marketplace, is a prominent example in this sector.
Section 5: Ethereum’s Transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
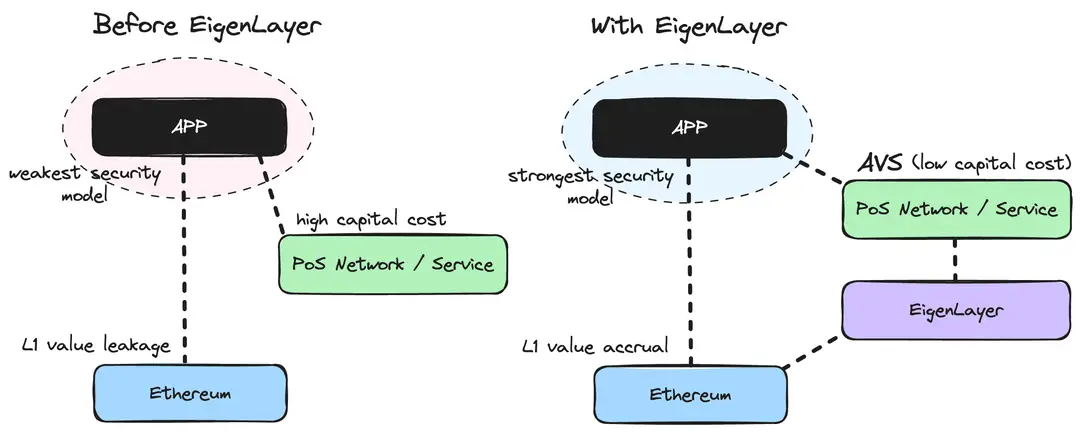
5.1 Transition to PoS
Ethereum's transition to Proof-of-Stake introduced new concepts like Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSD) and Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRT). Innovations such as EigenLayer have emerged, providing additional staking opportunities and leveraging Ethereum's security for new applications.
Section 6: Current Trends and Future Outlook
6.1 Multiple Chains and Cross-Chain Protocols
Interoperability and ease of use are increasing through advancements like account abstraction and intent-based transactions, making DeFi more accessible across different blockchain networks.
6.2 Rising Interest Rates and Real-World Assets (RWA)
The integration of real-world assets into DeFi is becoming more prominent, offering stable yields and diversified collateral options.
6.3 DeFi's Impact and Cycles
DeFi's innovation is cyclical, driven by advancements in both infrastructure and applications. Understanding these cycles is crucial for anticipating future developments.
Key Takeaways
DeFi revolutionizes finance with permissionless access, transparency, and interoperability via blockchain. Emerging from early blockchain experiments, it surged in 2020 with platforms like Uniswap, enabling widespread token creation and trading. Core components—stablecoins, DEXs, and lending protocols—redefine traditional financial services. Advanced concepts like composability and derivatives expand DeFi's scope. Ethereum's shift to Proof-of-Stake introduces new staking opportunities. Current trends emphasize multi-chain interoperability, real-world asset integration, and the cyclical nature of innovation. Builders and investors should explore SocialFi and enhance on-chain liquidity for Bitcoin to capitalize on DeFi's growth.
Q&A
1.Question 1: Besides DeFi, what other sectors are you bullish on?
Answer: Beyond DeFi, I recommend exploring SocialFi platforms like Forecaster. SocialFi is about building connections and communities in the crypto space, similar to how Facebook connects users. This sector is evolving and holds significant potential as it complements the existing financial system of DeFi by fostering community and cultural interactions.
2.Question 2: Within DeFi, which subcategory has been evolving the most and could be interesting for students and build-a-thon participants to explore?
Answer: I suggest focusing on Bitcoin assets. With the advent of Bitcoin ETFs, the number of Bitcoin holders is growing rapidly. There's a need for on-chain liquidity solutions to enable these holders to participate in DeFi scenarios, such as wrapped tokens and yield-bearing assets. This area offers many opportunities for innovation and can provide substantial value to Bitcoin holders by integrating them into the DeFi ecosystem.