Back
Complex Transactions
Sui
By HackQuest
Aug 14,20243 min readWelcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in a revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slang barriers preventing you from learning about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an essential concept in the world of Web3: [Complex Transactions].
What is Complex Transactions?
Complex transactions in the context of Web3 refer to sophisticated operations executed on blockchain networks, particularly through smart contracts. Unlike simple transactions that involve transferring cryptocurrencies between wallets, complex transactions involve multiple conditions, triggers, or steps that must be fulfilled for the transaction to execute autonomously.
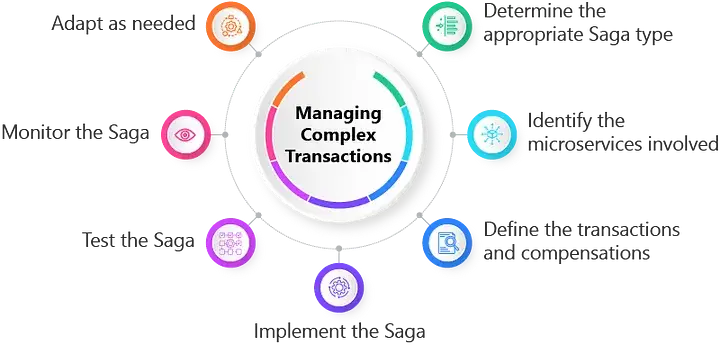
Source: Medium
Origin of Complex Transactions
The concept of complex transactions emerged with the advent of Ethereum and its introduction of smart contracts in 2015. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined terms written in code, allowing for the automation of complex processes without intermediaries. This innovation expanded the capabilities of blockchain beyond simple value transfers to include conditional transactions, multi-step operations, and automated decision-making.
How is the Term Used in Crypto?
In the crypto space, complex transactions are integral to decentralized applications (dApps) and various sectors:
●Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi platforms utilize complex transactions to facilitate lending, borrowing, yield farming, and trading activities. Smart contracts execute these operations based on predefined conditions, ensuring efficiency and transparency.
●Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFT platforms leverage complex transactions for minting, selling, and trading unique digital assets. Smart contracts manage ownership rights, royalties, and other conditions associated with NFT transactions.
●Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs use complex transactions to facilitate peer-to-peer trading of tokens without intermediaries. Automated market-making protocols execute transactions based on liquidity and pricing algorithms, enhancing trading efficiency.
Applications and Innovations
Beyond current use cases, ongoing innovations in blockchain technology are expanding the scope of complex transactions:
●Interoperability: Blockchain interoperability allows for complex transactions across different blockchain networks, enabling seamless asset transfers and interactions between ecosystems.
●Layer 2 Solutions: Scalability solutions like Layer 2 networks improve transaction throughput and reduce costs, enhancing the feasibility of complex transactions on Ethereum and other blockchains.
Challenges and Considerations
While complex transactions offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges:
●Security: Ensuring the security of smart contracts and mitigating risks associated with complex logic and conditions.
●Scalability: Handling increasing transaction volumes while maintaining network efficiency and low transaction costs.
●Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to evolving regulatory frameworks, especially concerning financial transactions and data privacy.
Conclusion
Complex transactions represent a fundamental advancement in Web3 technology, enabling decentralized networks to execute sophisticated operations autonomously. From DeFi protocols to NFT marketplaces and beyond, the versatility of smart contracts continues to redefine digital finance and application development.
If you would like to learn more about terms like API Node, let’s explore more in our HackQuest Web3 Glossary!