Back
Governance
Open Campus
By HackQuest
Nov 13,20245 min readWelcome to the Web3 world, where digital finance and applications are shown in a revolutionary way through the fusion of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and a pioneering spirit. Are you overwhelmed by the wealth of terms in the Web3 world that you don’t understand? Are those slang barriers preventing you from learning about Web3? Don’t worry! We’re here to explain the obscure terms to guide your learning. Today, we're diving into an essential concept in the world of Web3: [Governance].
What is Governance
In Web3, governance involves the processes and mechanisms for making and executing decisions within decentralized networks. This evolving field uses technologies like smart contracts and consensus algorithms to facilitate decision-making. Unlike centralized systems with a single authority, Web3 promotes a democratic and inclusive approach, empowering communities and reducing reliance on central authorities.
Smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements encoded directly into the blockchain, automate decision-making, ensuring transparency and immutability. They allow stakeholders to vote on proposals and enforce rules without intermediaries.
Consensus algorithms establish trust and agreement within decentralized networks by determining how participants reach consensus on proposed changes or decisions.

Source: CoinDesk
Types of Governance Models
On-chain Governance
On-chain Governance marks a significant shift in decision-making by conducting votes directly on the blockchain using smart contracts and token-based systems. Network participants, typically token holders, propose and vote on protocol changes, with voting power often proportional to their token holdings, creating a democratic yet token-weighted process.
A major advantage of On-chain Governance is its transparency and immutability, as all decisions and votes are recorded on the blockchain, making them auditable and resistant to tampering. However, scalability and efficiency can be challenging, especially in larger networks with frequent decision-making needs.
Off-chain Governance
Off-chain Governance complements on-chain mechanisms by involving external factors and decision-makers. Although decisions aren’t made directly on the blockchain, stakeholders such as developers, community members, and third-party experts influence them. Discussions and proposals typically occur in forums, on social media, or dedicated platforms.
The key advantage of Off-chain Governance is its flexibility, allowing for quicker adaptation to changes. However, it may lack the transparency and immutability of on-chain models. To maintain legitimacy, off-chain governance must encourage inclusivity and open communication among participants.
In Web3, a hybrid approach combining on-chain and off-chain elements is becoming more common, balancing decentralization with efficiency as the community navigates complex decision-making landscapes in decentralized systems.
Case: Open Campus Governance
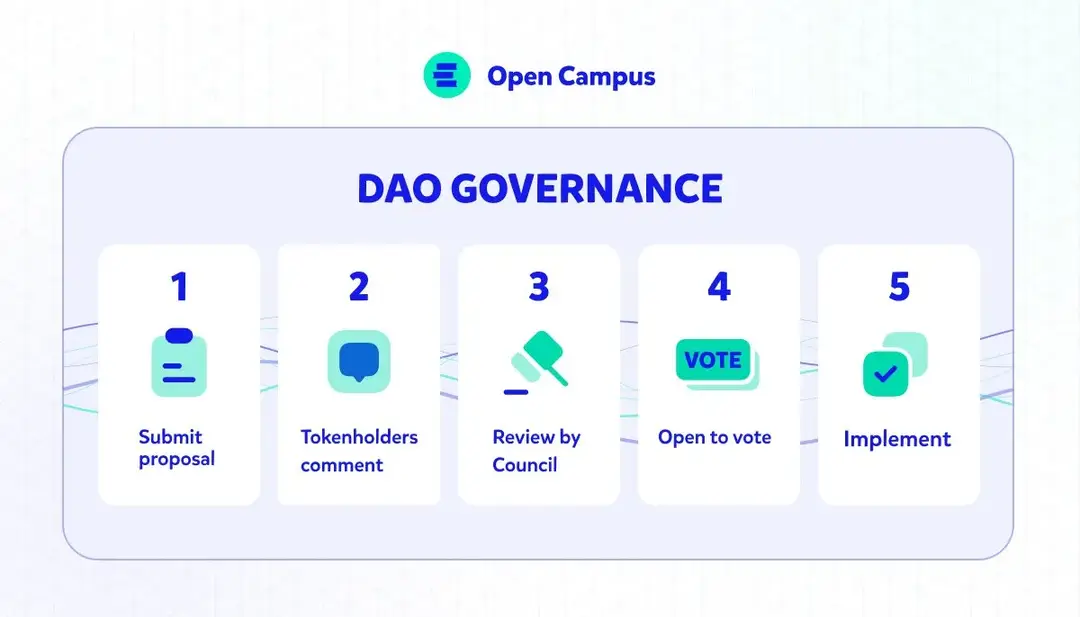
Source: Medium
Open Campus, a trailblazer in digital education, is advancing towards decentralization by forming a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). The Open Campus DAO empowers the community to govern the project’s future through collective decision-making. This initiative signifies a pivotal milestone, emphasizing the importance of community involvement and the collective intelligence of its EDU holders.
Learn more key features of the Open Campus DAO in this article:
By leveraging blockchain technology, the DAO operates autonomously, ensuring fairness and inclusivity in decision-making. This decentralized model marks a paradigm shift from traditional hierarchical governance, reinforcing Open Campus's commitment to transparency and community-driven progress.
Importance of Governance in Web3
Transparency
Open, verifiable transactions are fundamental to decentralized systems, fostering trust among participants by ensuring that all decisions and actions are transparent to stakeholders. With blockchain technology providing an immutable record, users can examine every transaction, promoting accountability and minimizing the risk of fraud. In an environment where trust is crucial, the transparency inherent in Web3 governance stands as a beacon of reliability.
Inclusivity
Web3 governance models emphasize inclusivity, ensuring broad participation in decision-making. These decentralized processes invite contributions from diverse stakeholders, not just a select few. Token-based voting mechanisms enable even minor participants to have a say, preventing decision-making from being dominated by a privileged minority. This inclusive approach aligns with the democratic principles of the digital era, empowering all members and fostering a sense of ownership within the decentralized ecosystem.
Adaptability
Web3 governance thrives on its flexibility. Unlike rigid centralized structures, decentralized systems can adapt to evolving needs and circumstances. Smart contracts and on-chain proposals facilitate quick changes to rules and protocols, which is vital in the ever-changing digital landscape. This adaptability ensures that Web3 remains responsive and resilient, allowing it to address new challenges and opportunities effectively. The ability to adjust and iterate is a defining feature of Web3 governance, maintaining its relevance and effectiveness for the future.
Challenges
Voter Apathy
In the dynamic world of Web3 and decentralized systems, voter apathy poses a significant challenge to governance. Despite the democratic potential, many participants remain disengaged due to system complexity, lack of incentives, and information overload. Addressing this issue is vital for the healthy functioning of decentralized ecosystems. Simplifying participation, providing rewards, and fostering a sense of community ownership can effectively combat voter apathy, ensuring more active and equitable governance in Web3.
Sybil Attacks
In the decentralized Web3 landscape, Sybil attacks pose a serious threat, where a malicious actor creates multiple fake identities to manipulate voting and decision-making processes, undermining governance integrity. To prevent these attacks, innovative solutions such as identity verification and reputation-based systems are essential. These measures enhance trust and security, ensuring each participant's voice is authentic and maintaining the integrity of decentralized decision-making processes.
Future Outlook
In the rapidly evolving Web3 landscape, decentralized systems powered by blockchain technology and smart contracts are revolutionizing governance. Traditional hierarchies are being replaced by transparent, community-driven decision-making processes. Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) holds exciting potential. AI can automate decision-making, enhancing efficiency and impartiality by analyzing vast data sets to inform governance decisions, thus improving transparency and reducing bias.
Advanced governance models are also emerging. While many decentralized systems currently use token-based voting, which has its limitations, future models might incorporate quadratic voting, where the influence of a vote increases with the voter’s stake, or futarchy, which uses market predictions to guide decisions. These innovative models aim to align decisions with the community's collective interests more accurately.
The future of Web3 governance is both promising and dynamic. With AI integration and the development of advanced governance models, decentralized systems are set to become more efficient, transparent, and equitable. This governance revolution in the Web3 ecosystem has the potential to redefine decision-making processes in the digital age.
Conclusion
As we navigate the transformative world of Web3, governance stands as a crucial element in shaping decentralized networks. The integration of smart contracts and consensus algorithms facilitates transparent, community-driven decision-making, contrasting sharply with traditional centralized systems. On-chain and off-chain governance models each offer unique strengths, and a hybrid approach is increasingly seen as a balanced solution.
Case studies like Open Campus DAO highlight the potential of decentralized governance to foster inclusivity, transparency, and adaptability. Despite challenges such as voter apathy and Sybil attacks, innovative solutions are being developed to ensure robust and fair governance.
Looking to the future, the incorporation of AI and advanced governance models promises to enhance efficiency and impartiality in decision-making processes. The ongoing evolution of Web3 governance holds the potential to redefine how decisions are made in the digital age, ensuring a more equitable and transparent ecosystem for all participants. The journey towards decentralized governance is a beacon of innovation, paving the way for a more inclusive and dynamic future in the digital realm.