Back
Revocation
EAS
By HackQuest
May 29,20243 min readWelcome to the world of Web3, where cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and a unique culture converge. Entering the world of Web3 can be both thrilling and overwhelming, especially when faced with the seemingly cryptic language used by enthusiasts. Don't worry if you feel they sound like some secret codes, we are here to unravel their meaning. In this article, we are going to introduce [Revocation].
What is Revocation?
Revocation refers to the process of marking an attestation as invalid. Attestations are statements or assertions certified by a party (the attestor), and revocation is necessary when these are no longer accurate or valid. The primary purpose of revocation is to maintain the integrity and relevance of the attestations within systems that rely on current and accurate data.
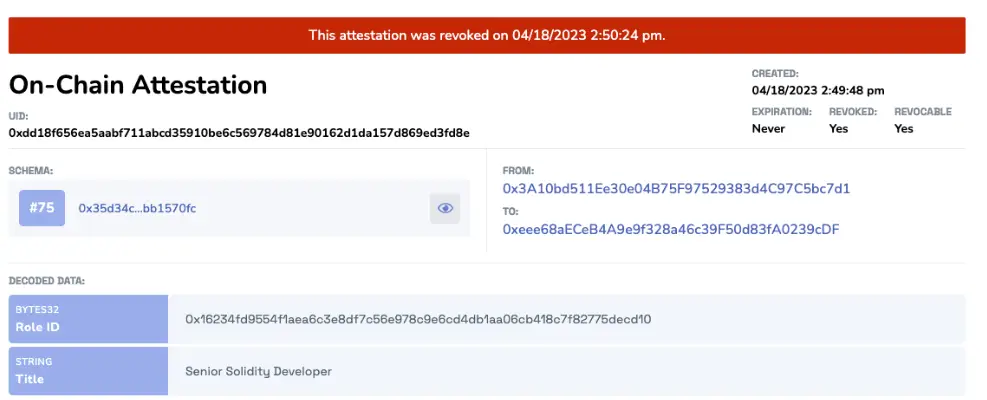
How Does Revocation Work?
Revoking an attestation changes its status from "valid" to "revoked" by updating a specific field—usually termed as 'revoked'—to true. This alteration is critical for systems that need to reflect real-time changes, ensuring that any reliance on the attestations is based on the most recent and correct information. The process can be performed either on-chain, using blockchain technology, or off-chain, through manual or software-enabled methods.
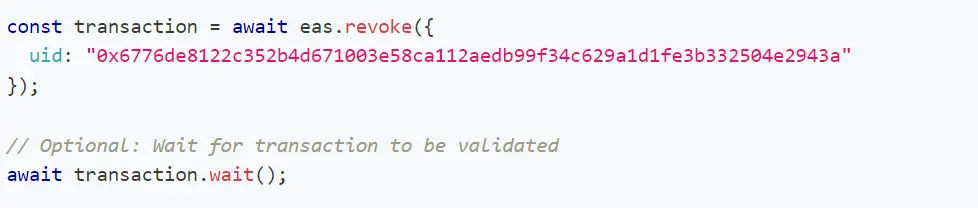
The Backstory of Revocation
Revocation emerged from the need for accurate and reliable data handling in digital security systems, initially seen in the centralized management of certificates and credentials.
As digital ecosystems evolved and blockchain technology introduced decentralized frameworks, smart contracts became essential for revoking attestations in an automated and transparent manner. These developments allowed organizations to swiftly invalidate outdated or incorrect credentials, ensuring secure access and up-to-date identity verification. With the rise of decentralized applications, DAOs, and complex supply chains, revocation became indispensable for maintaining trust. Frameworks like the Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS) and software development kits (SDKs) have further refined the process, offering standardized and seamless on-chain and off-chain attestation management, thereby reinforcing security, accuracy, and scalability in modern digital systems.
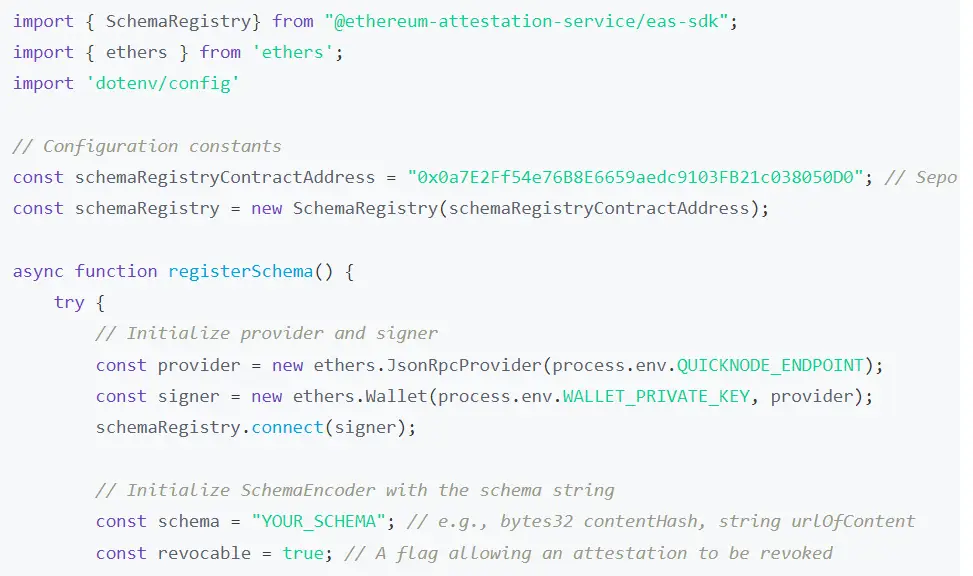
Use Case of Revocation
In the context of Web3, revoking attestations is essential to ensure integrity and accuracy across decentralized systems. Here are a few examples featuring the use cases of revocation.
●Governance and Voting
In decentralized governance systems, such as those used by DAOs, members receive attestations that enable them to vote or participate in decision-making. When a member’s eligibility status changes—due to role change, expiration of membership, or detected misconduct—their attestation should be revoked to prevent unauthorized participation and ensure voting integrity.
●Token Access and Permissions
Some Web3 projects grant specific tokens to participants that represent access to certain features or roles. If these tokens are linked to an attestation, and a participant's eligibility changes, revoking the attestation tied to that token prevents misuse of access or manipulation of permissions.
●DeFi Collateral
In decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, users provide attestations when locking up assets as collateral. If the value or state of these assets becomes non-compliant or changes, the attestation should be revoked to prevent false borrowing or misreporting of asset values, ensuring the financial system remains trustworthy.
Conclusion
Revocation is a crucial mechanism within systems utilizing attestations, such as blockchain environments or digital credentialing platforms. It ensures the validity and reliability of the data or statuses represented by attestations, catering to dynamic conditions or rectifying errors. Revoking both on-chain and off-chain attestations offers flexibility and control over the lifecycle of attestations, safeguarding the interests and operational integrity of entities relying on these attestations. Wanna know more about revocation of attestations? Check out HackQuest’s EAS Learning Track for more details and insights.