Introducing GasGuard, a decentralized intelligence subnet that predicts gas costs and execution failure risks for complex DeFi transactions before they are executed, helping users avoid consequences

A decentralized intelligence subnet that predicts gas cost, execution failure risk, and safety for complex composed DeFi transactions using miner-submitted simulations and validator-enforced scoring.
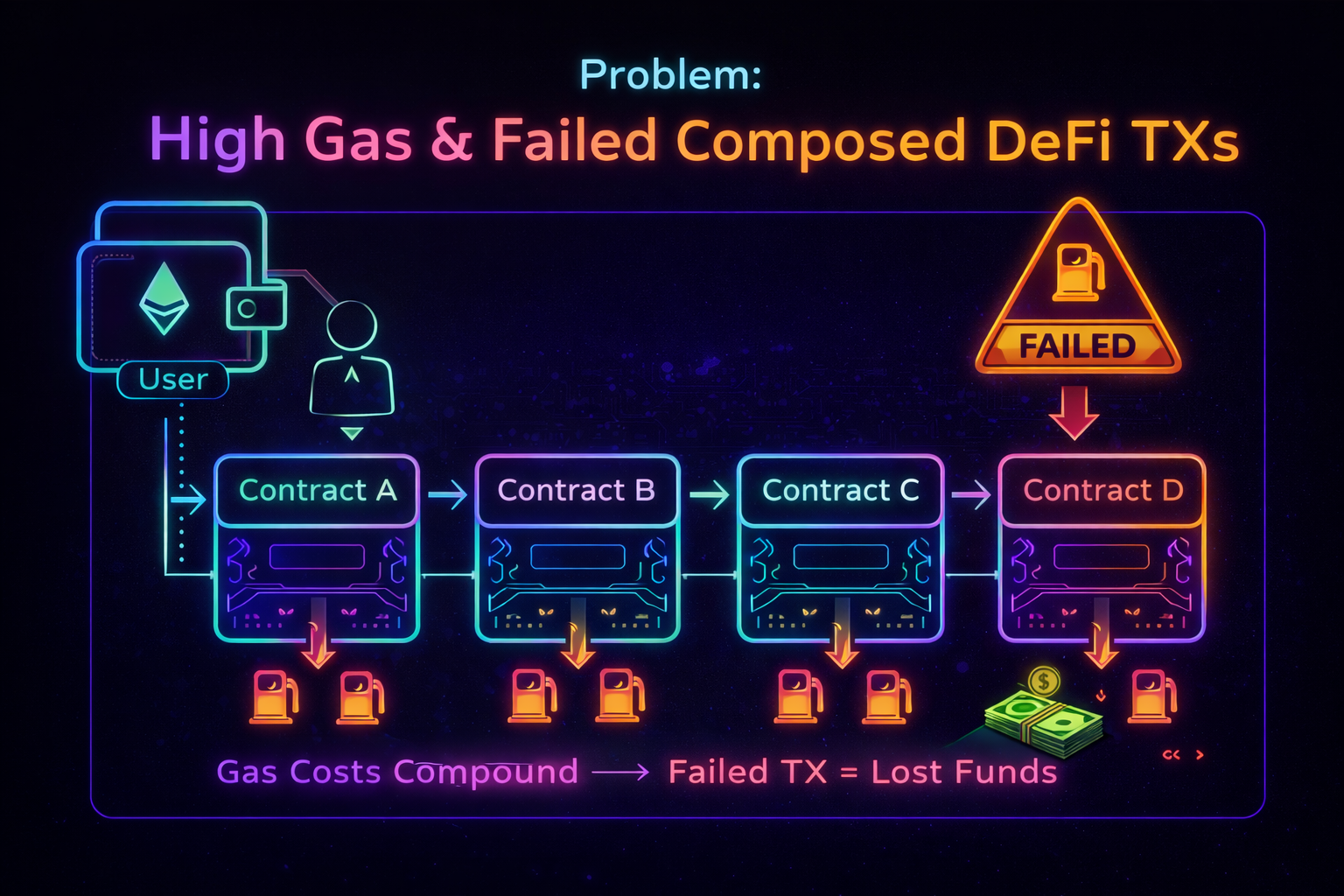
DeFi composability is powerful but costly. As transactions span multiple protocols, gas usage becomes unpredictable, failures increase, and users lose funds. GasGuard transforms this uncertainty into actionable execution intelligence.
Description
In composed transactions, users interact with multiple smart contracts in a single execution.
User
→ Contract A
→ Contract B
→ Contract C
→ Contract D
Each interaction introduces:
Function dispatch overhead
Context switching
Validation logic
Storage access
Impact
Gas costs grow rapidly
Execution becomes inefficient
Users pay more for the same intent
Description
Independent protocols repeatedly perform the same checks:
Balance verification
Permission validation
Storage reads
Even when these checks were already performed earlier in the same transaction.
Impact
Duplicate computation
Wasted gas
No shared standards to reuse validations
Description
Storage writes (SSTORE) are among the most expensive EVM operations.
In composed transactions, protocols often:
Update balances in multiple contracts
Persist intermediate states
Overwrite the same storage slots multiple times
Impact
Gas usage spikes
Transactions hit block gas limits
Failed transactions still burn gas
Local gas optimizations within individual protocols
Layer 2 rollups (lower cost, same structural problems)
Manual batching by developers
System-level understanding of composed transactions
Cross-protocol gas coordination
Predictive tooling to prevent failures before execution
Shared optimization standards
Current tools react after failure.
GasGuard acts before execution.
GasGuard does not try to rewrite DeFi protocols.
Instead, it provides execution intelligence that enables better decisions.
It addresses each problem with a specific solution class.
Transaction Bundlers
What it does
Analyzes multi-step transactions
Collapses multiple calls into a single optimized execution plan
Minimizes external calls and storage writes
Outcome
Fewer contract hops
Lower gas consumption
More efficient execution
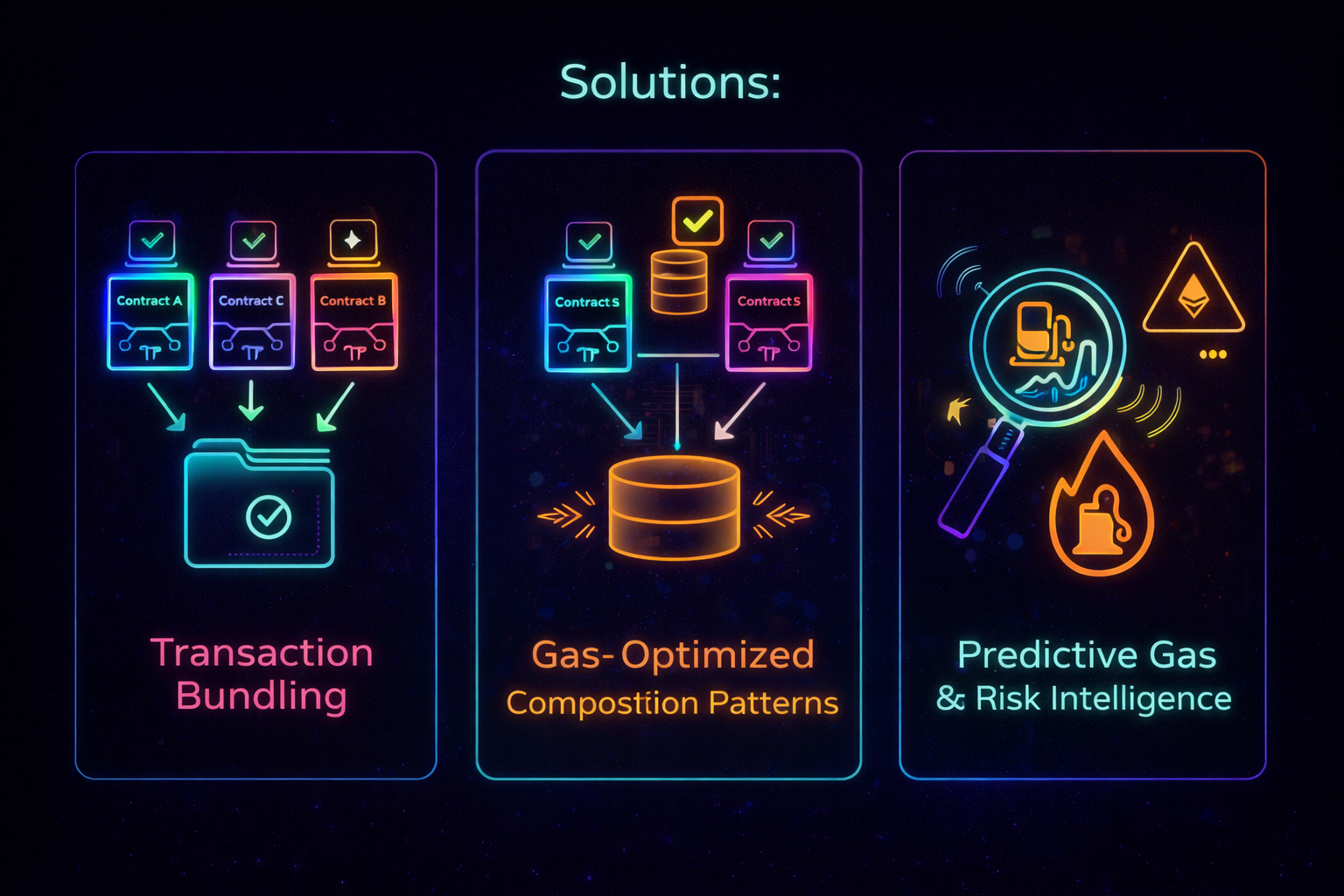
Gas-Optimized Composition Patterns
What it does
Defines reusable standards for:
Shared validation logic
Stateless intermediate execution
Shared execution context
Outcome
Eliminates redundant checks
Reduces repeated storage reads
Improves composability efficiency
Predictive Gas Estimation & Risk Intelligence (Primary Focus)
What it does
Simulates full composed transactions
Detects storage-heavy execution paths
Predicts gas usage and failure probability
Warns users before execution
Outcome
Fewer failed transactions
Reduced wasted gas
Higher user trust
Transaction Analyzer
↓
Gas Simulation Engine
↓
ML-Based Risk Analyzer
↓
User Warning / Recommendation
👉 https://app.eraser.io/workspace/NkHOTU5CX8bUGDV0pzDZ
Transaction Analyzer
Extracts call depth, protocol types, storage operations
Gas Simulation Engine
Runs dry-run simulations on forked state
ML-Based Risk Analyzer
Predicts failure probability and risk class
Learns from historical transaction outcomes
User Warning Layer
Converts predictions into actionable guidance
Gas cost estimates
Failure probability scores
Risk classification (Low / Medium / High)
Failure reason attribution
This intelligence is:
Non-trivial
Computation-heavy
Continuously improvable
User submits transaction payload
↓
Miners simulate & analyze
↓
Validators evaluate prediction quality
↓
Rewards distributed based on accuracy & effort
Who earns rewards
Miners → accurate, timely predictions
Validators → honest, correct scoring
Reward factors:
Reward ∝ Accuracy × Confidence × Timeliness × Reputation
Miners
Must run real simulations
Must produce calibrated predictions
Low-quality or spam outputs are penalized
Validators
Score miner outputs against ground truth
Penalized for dishonest or collusive behavior
Compete with other validators
Simulation
Feature extraction
Model inference
Cannot be cheaply faked
Better heuristics → better rewards
Better models → higher reputation
Learning compounds over time
Validator publishes transaction payload
Miners simulate and predict outcomes
Validators compare predictions
Scores computed using accuracy + calibration
Rewards distributed per epoch
Tasks
Simulate composed transactions
Predict gas and failure risk
Input
Encoded calldata
Chain context
Output
{
"estimatedGas": uint,
"failureProbability": float,
"riskLevel": enum,
"confidence": float
}
Performance Metrics
Accuracy
Calibration
Speed
Consistency
Evaluation
Reference simulations
Cross-miner comparison
Consensus-weighted scoring
Cadence
Per epoch
Rolling history
Incentives
Honest scoring rewarded
Malicious behavior penalized
Millions lost to failed gas fees
No neutral execution-risk oracle exists
Centralized estimators
Wallet heuristics
Protocol-specific tools
❌ None are decentralized, composable, and incentive-aligned.
Initial Users
DeFi power users
Wallet developers
Yield aggregators
Distribution
Wallet plugins
APIs
Dashboards
Bootstrapping
Boosted early rewards
Free risk queries
Validator incentives
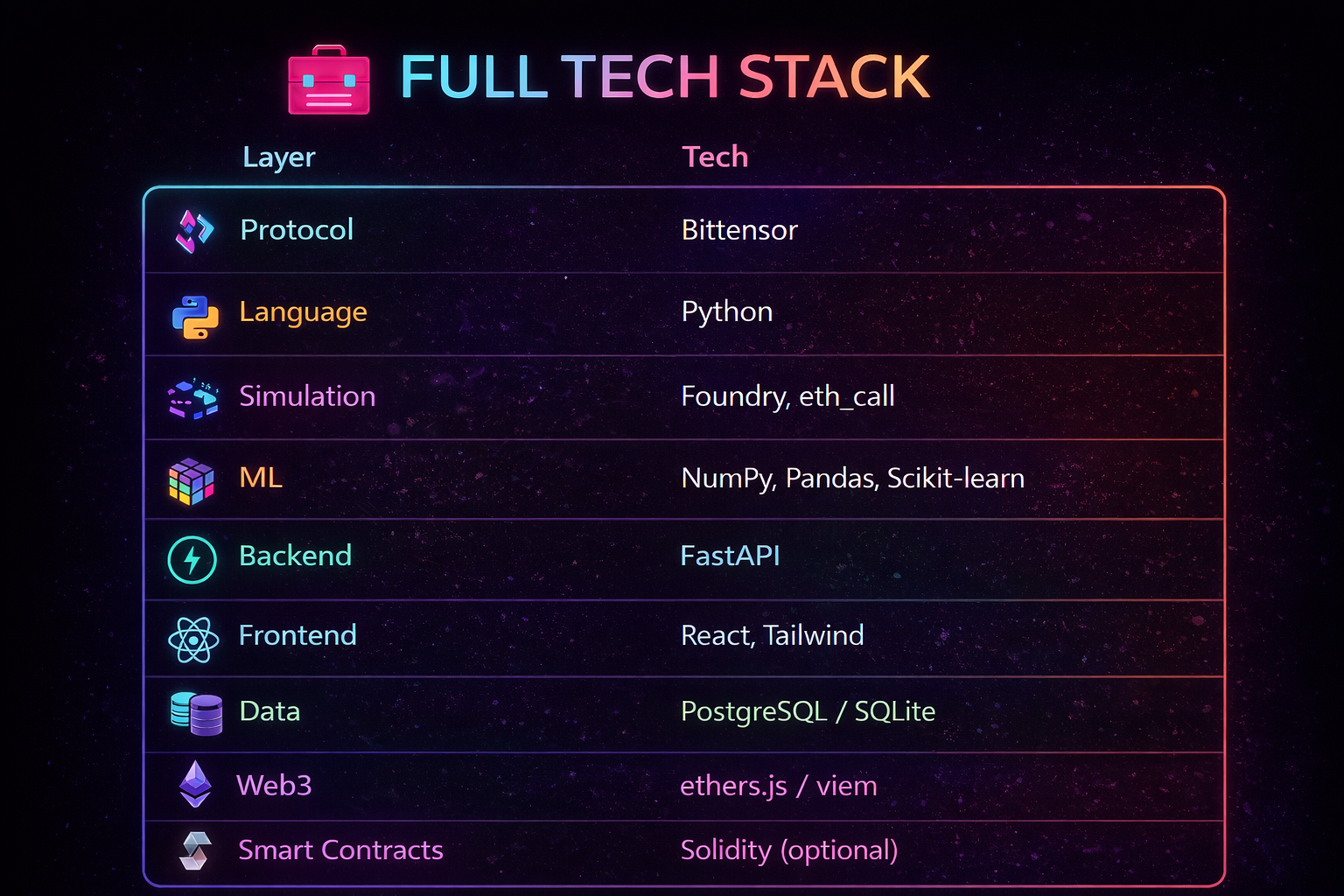
Tech Stack
Final Project Structure(Textual Representation)
GasGuard Subnet
├── Problem: High gas & failed composed DeFi TXs
├── Solutions:
│ ├── Transaction Bundling
│ ├── Gas-Optimized Composition Patterns
│ └── Predictive Gas & Risk Intelligence
├── Architecture:
│ ├── Analyzer
│ ├── Simulator
│ ├── ML Risk Engine
│ └── User Warnings
├── Incentive Design (Miners + Validators)
├── Proof of Intelligence & Effort
├── Business & Market Rationale
├── Go-To-Market Strategy
└── Long-Term Adoption Vision
Final Project Structure(Visual Representation)

GasGuard is currently in the ideation phase
Not raised