NTU MOOC Study Notes - Session 15 Why AI Needs Decentralisation: Retaining Economic Agency in the AI-powered Future
Date: 10-11 AM SGT, October 7th 2024 / 10-11 PM EST, October 7th 2024
Session Title: Why AI Needs Decentralisation: Retaining Economic Agency in the AI-powered Future
NTU I&E x HackQuest MOOC is free and open to all individuals interested in Web3. This session will explore the convergence of AI and Blockchain, highlighting how DAI promotes transparency, minimizes bias, and lays the groundwork for a future characterized by shared intelligence. The discussion will be led by Julian Peh, Founder and CEO of KIP Protocol.
For those who prefer having a text summary and review material, this study note provides a recap of what’s covered during the MOOC. Happy learning!
Overview
Main Topic: Why AI Needs Decentralisation: Retaining Economic Agency in the AI-powered Future
AI has been one of the hottest trends and narratives over the last few years. The revolutionary technology carries immense potential but also significant centralization risks in the meantime. This session focuses on the intersection of AI and Blockchain, introducing users to how DAI fosters transparency, reduces bias, and paves the way for a future of shared intelligence.
Objectives:
Section 1: Introduction to Decentralized AI
The shift to an AI+Human era marks a transformative stage where AI is integrated across all layers of technology, fundamentally altering work and personal interaction. The era of human-only innovation has evolved into AI-human collaboration that enhances productivity and creativity.
The Dark Side of AI

Centralized AI monopolies create unique risks, making decentralization essential to avoid a future dominated by monopolistic control:
Decentralized AI, enabled by Web3, is essential to break the closed structure of centralized AI, fostering an open, fair, and competitive ecosystem where users retain control and ownership.
Section 2: Core Components of Decentralized AI Ownership
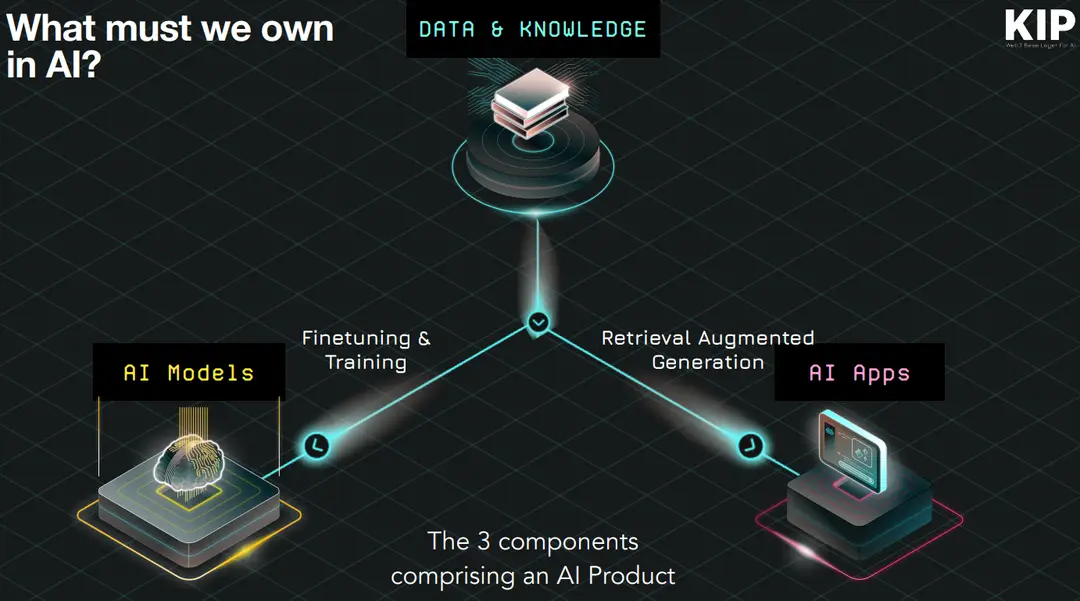
AI value creation hinges on three core components:
Ownership through Web3
To counter monopolistic control, KIP Protocol leverages Web3 to enable ownership and secure property rights over these AI components. Following the “Bundle of Rights” theory, KIP Protocol ensures ownership that includes the right to use, monetize, exclude others, transfer, manage, and destroy AI assets and data. Decentralizing ownership enables digital property rights, ensuring user control within the AI ecosystem.
In contrast to centralized ownership by tech giants, Web3 offers a “Read-Write-Own” internet where users assert ownership over AI models, data, and applications. This aligns with the vision of a decentralized AI future, preserving economic and creative agency for all stakeholders.
Section 3: KIP Protocol Framework for AI Decentralization
KIP Protocol addresses three major challenges in building a decentralized AI ecosystem: ownership, connectivity, and settlement. Each layer of the protocol solves a specific issue essential for decentralized AI.
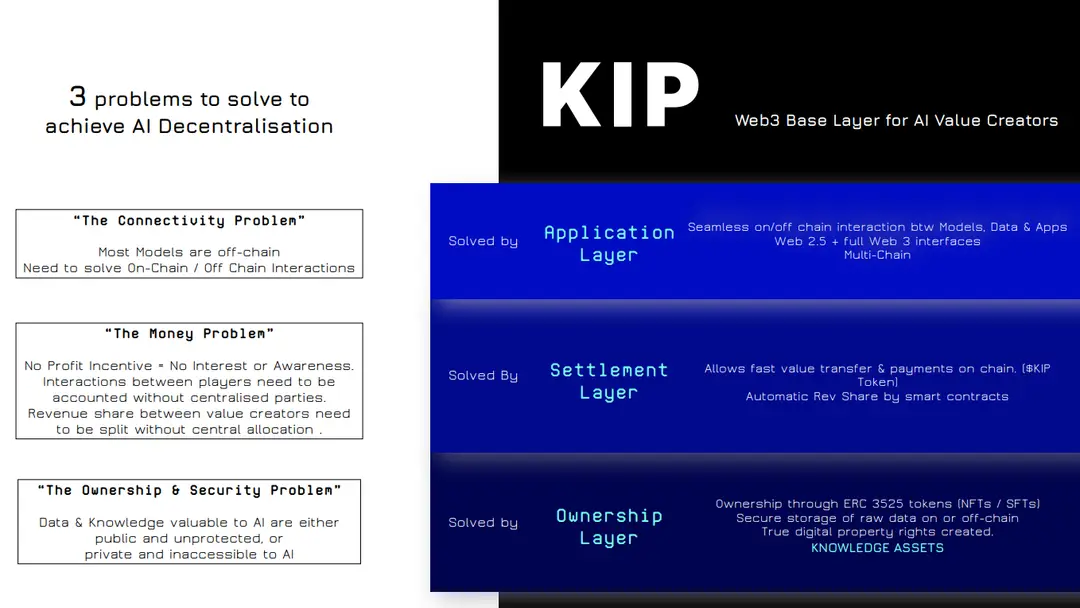
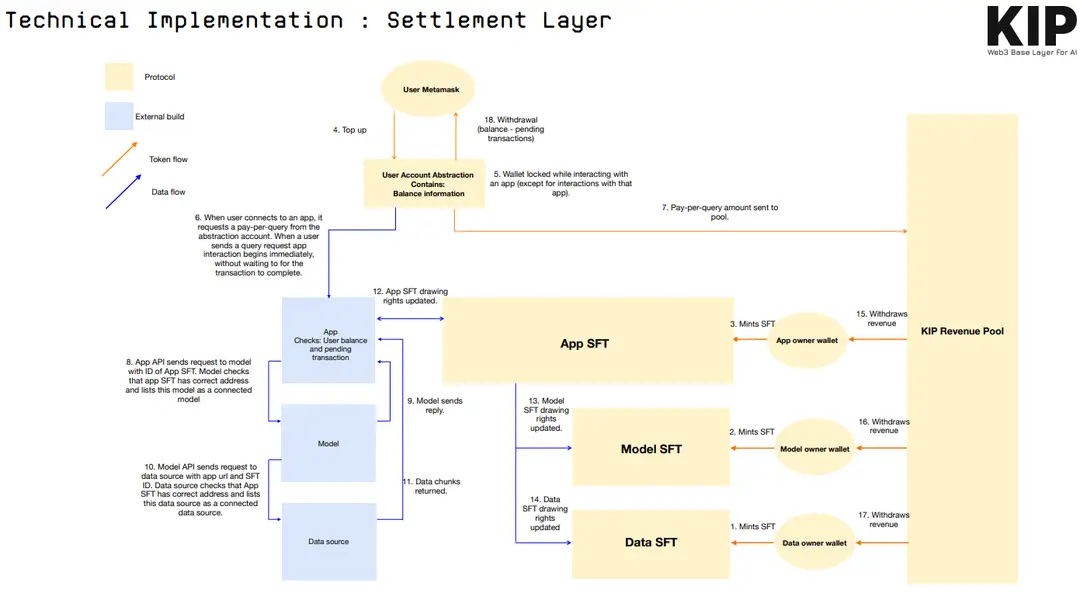
Technical Implementation:
The “free flow of data and revenue” across decentralized AI components is fundamental to sustaining the value of decentralized AI, ensuring all parties are adequately rewarded and incentivized to participate.
Section 4: Case Studies in Decentralized AI
4.1 Moemate.ai: AI Companions in Entertainment
KIP Protocol’s partnership with Moemate.ai illustrates how decentralized AI can reshape entertainment by granting users ownership over virtual AI companions. Moemate offers AI-generated virtual companions, often styled as virtual partners or friends, with over 4 million users in Web2. To provide users with more control and a share in the value created through their AI interactions, Moemate sought to transition to Web3.

KIP’s Role:
Moemate serves as a “bridge” between Web2 and Web3, demonstrating the potential of decentralized AI to expand into mainstream consumer products by empowering users with ownership.
4.2 Open Campus University: AI in Decentralized Education
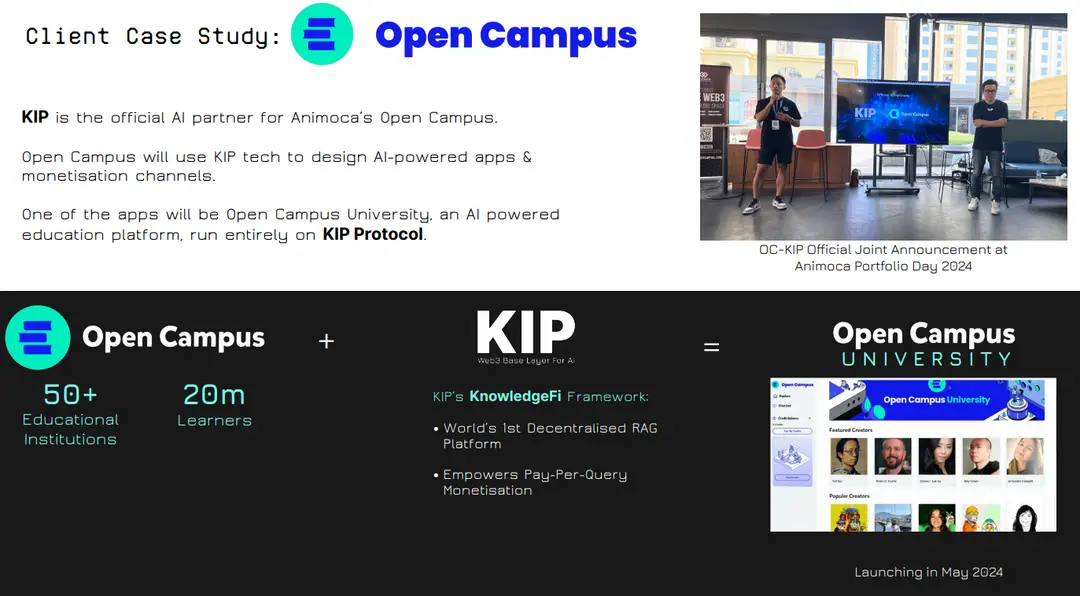
KIP Protocol’s collaboration with Animoca to create Open Campus University highlights AI’s transformative potential in education. Designed as a decentralized Coursera, Open Campus University leverages AI to deliver interactive, personalized learning experiences with features like AI-powered study companions, quiz generators, and citation finders.
KIP’s KnowledgeFi Framework:
Revenue Model:
Through a pay-per-query model, Open Campus University ensures fair revenue distribution among creators of educational content, such as professors and content providers, as well as the model providers. This revenue-sharing mechanism sustains a self-sustaining decentralized education ecosystem, offering teachers, institutions, and students an economic stake in the platform.
The decentralized structure of Open Campus provides educators and students with a stake in the platform, aligning with KIP Protocol’s mission to empower individuals through decentralized ownership.
Section 5: Q&A Session
Q1: What are the risks of centralized AI monopolies?
Centralized AI monopolies present dangers by holding excessive power through recursive improvement, data capture, and regulatory control. This power concentration allows monopolistic AI systems to influence public behavior, restricting fair competition.
Q2: How does decentralized AI work in practice?
KIP’s framework tokenizes AI models, data, and applications, allowing users and creators to interact transparently. For instance, a study companion on Open Campus University utilizes a decentralized model that securely accesses data on demand, offering students high-quality educational content without centralized control.
Q3: What differentiates KIP from other decentralized AI projects?
KIP Protocol focuses on rapid deployment, real-world partnerships, and solving practical issues like ownership, connectivity, and settlement. This approach enables existing AI platforms to adopt decentralized frameworks quickly, facilitating user control and sustainable monetization.
Q4: Is KIP hiring?
Yes, KIP Protocol is expanding across multiple departments to support its decentralized AI projects.
Q5: How does KIP view AI in education?
KIP provides tools enabling educators to create AI-powered educational resources that students engage with independently. The focus is on adaptive and mastery learning, envisioning a future where each learner has a personalized AI mentor that tailors content delivery to their pace and understanding.
Key Takeaway:
KIP Protocol demonstrates that a decentralized AI ecosystem is achievable and necessary to protect against monopolistic control and ensure equitable access to and ownership of AI assets. Through innovative partnerships and its KnowledgeFi framework, KIP enables secure, transparent, and monetizable AI interactions that empower users across sectors, from entertainment to education. KIP envisions a future where AI assets are user-owned, creating an inclusive AI ecosystem that supports economic and creative agency for all.